Description
Many multilevel inverter topologies have been introduced to address different types of applications. In this project we are designing a novel bidirectional t-type multilevel inverter for electric vehicle applications
Abstract
This paper presents a new integration of the five levels t-type multilevel inverter with a modified bi-directional dc-dc multilevel converter for electric vehicle applications. While the t-type mli utilize more power, switches compared to the conventional voltage source inverter. It generates a higher number of output voltage levels utilizing power switches with half of the peak inverse voltage. However, if such converter is connected to a conventional bi-directional dc-dc converter, the converter power switches have to be designed to withstand the full voltage of the dc bus. Moreover, such conventional configuration needs an addition of voltage balance circuit or special switching pattern with feedback and control loops to insure the voltage balance of the dc capacitors.
Introduction
This paper introduces a new configuration of bi-directional multilevel converter in electric vehicle (ev) applications. It has multilevel dc-dc converter with a direct current (dc) link capacitor voltage balance feature. Conventionally, from the propulsion system design point of view, the dc input power source is connected to the bi-directional dc-dc converter, which controls the voltage of the dc bus. The voltage balancing circuit is placed between the output of the dc-dc converter and the input of the multilevel inverter
The t-type mli utilize more power switches compared to the conventional voltage source inverter. It generates a higher number of output voltage levels utilizing power switches with half of the peak inverse voltage. However, if such converter is connected to a conventional bi-directional dc-dc converter, the converter power switches have to be designed to withstand the full voltage of the dc bus.
Existing system
- Conventional dc-dc converters are very reliable in controlling the dc bus voltage, it is not always the case when are connected to a multilevel inverter, as mentioned, multilevel inverter that is connected to a single dc power source is relying on split capacitor as an input stage to produce its sub-level output voltages. Such arrangement is susceptible to unbalanced capacitor voltages and hence voltage deviation of the neutral point. Therefore, an extra circuitry with or without control loop is to be added to ensure a balanced voltage on the capacitors and balance the neutral point. Another solution is applying a modified switching scheme.
- Many techniques are presented to control the capacitor voltages and the neutral point in split capacitor based multilevel inverters. The modified modulation-based techniques do not require adding an extra component in terms of power components (active/passive switches, capacitor and/or inductors). Thus, it has been seen as an optimum solution. However, it requires adding extra sensors and control loops if a wide range of operation and fault tolerance are to be achieved. Moreover, their ability to control and equalize the capacitors? voltages are limited by the redundancy states that are offered by the construction of multilevel converter itself.
Proposed system
The multilevel dc-dc boost converter originally introduced in can only operate as uni-directional boost converter which make it impractical in electric machine drive applications especially in ev. Therefore, the proposed converter configuration modified its structure by replacing the clamping diodes connected with ????????by two active power switches. These two switches are operated in a complementary manner and in conjunction with the boost converter synchronous switches. So, the simplicity of the original contracture is reserved as well as the number of controlling signals. Therefore, the proposed converter configuration is able to achieve a bi-directional operation where the input voltage is boosted in motoring mode, and the combined capacitors? voltage is bucked in breaking (regenerative) mode.
Advantages
No extra isolated sensor, control loops and/or special switching pattern are required. Moreover, the proposed configuration due to the high frequency cycle-by-cycle voltage balance between ???????? and ???????? the bulky electrolytic capacitors used in t-type mli are replaced with longer life more reliable film capacitors. This will result in a size and weight reduction of the converter by 20%. This allows more real estate for the ev battery in the chassis? space envelope; to increase its capacity.
Application
Proposed configuration in electric vehicles drive applications.
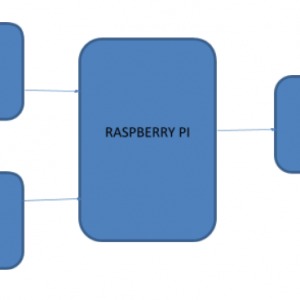
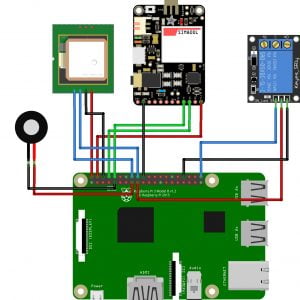
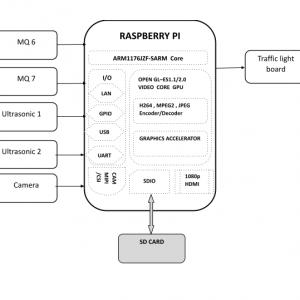
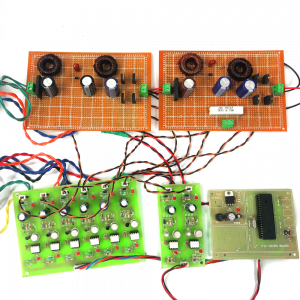
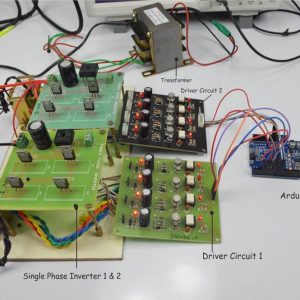
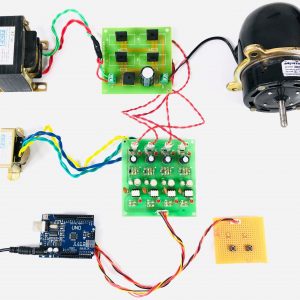
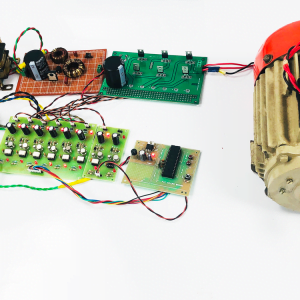
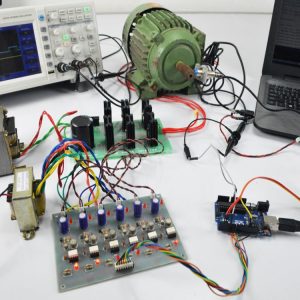
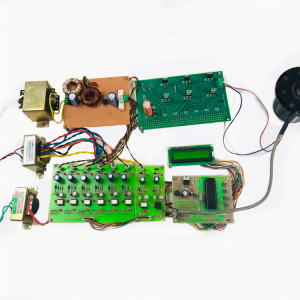
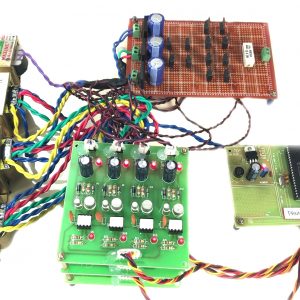
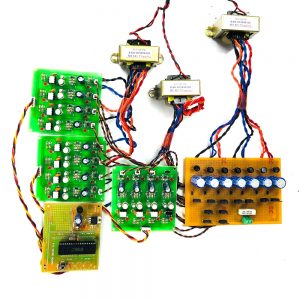
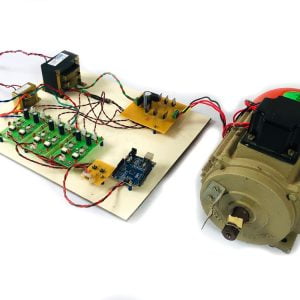
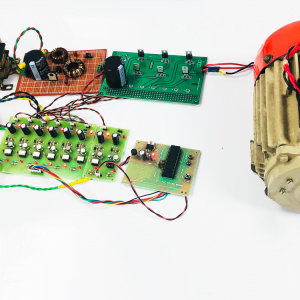
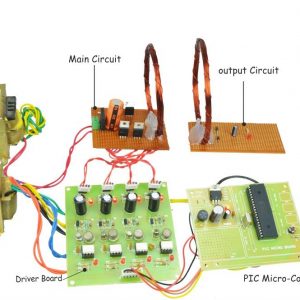
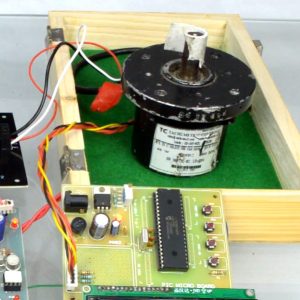
Block diagram
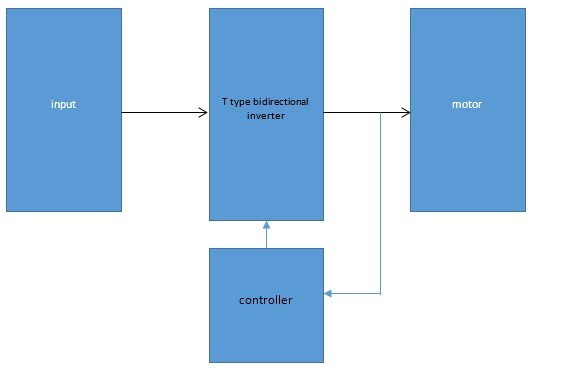
- Input
Concept of this project mainly focus on renewable energy sources like solar energy, fuel cell source etc.
- Main circuit
Induction motor driver circuit with t? type structure and bidirectional capability.
- Controller
Brain of the circuit, which will control all the functions of the circuit, all the modes of this circuit perfectly achieved by the controller
- Feedback
For having a stabilized output closed loop data has selected which will transfer the instant values of output data to the controller.
- Output
Ports can supply power to motor
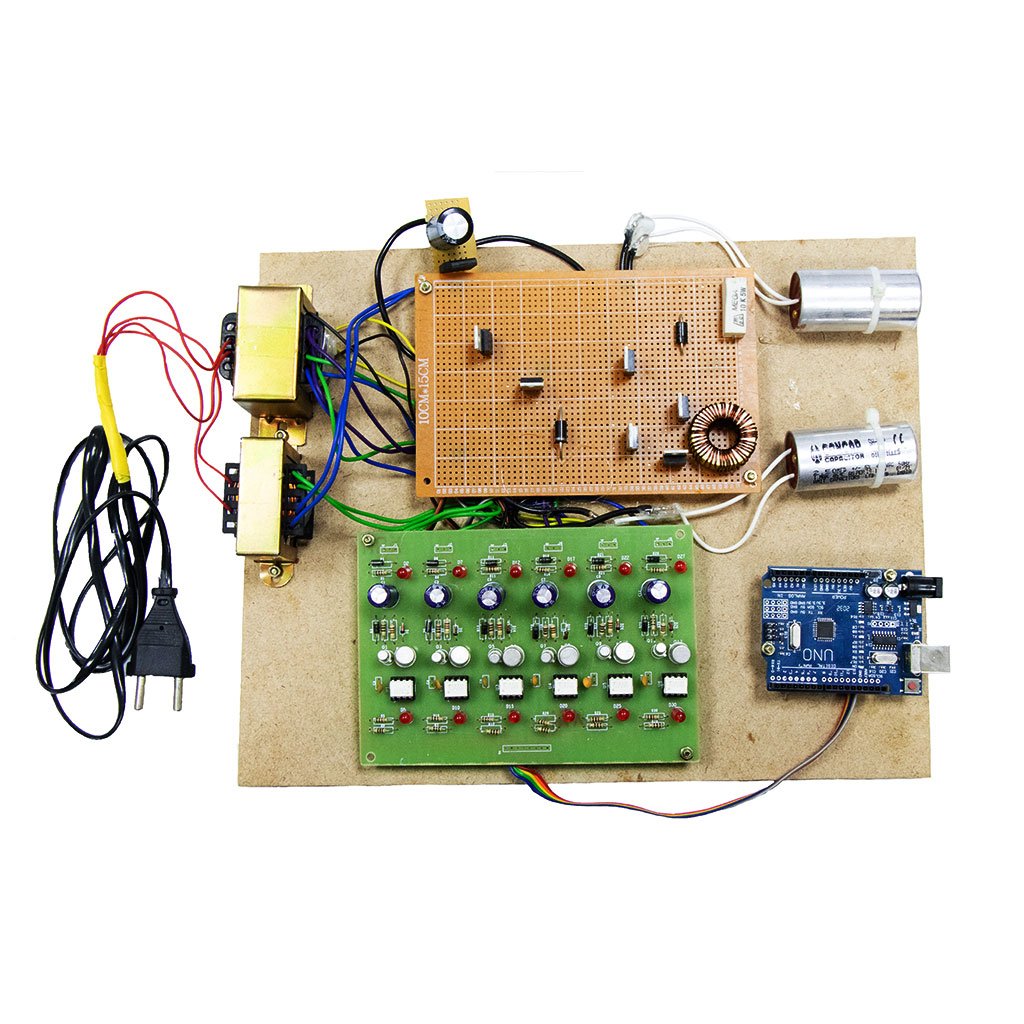
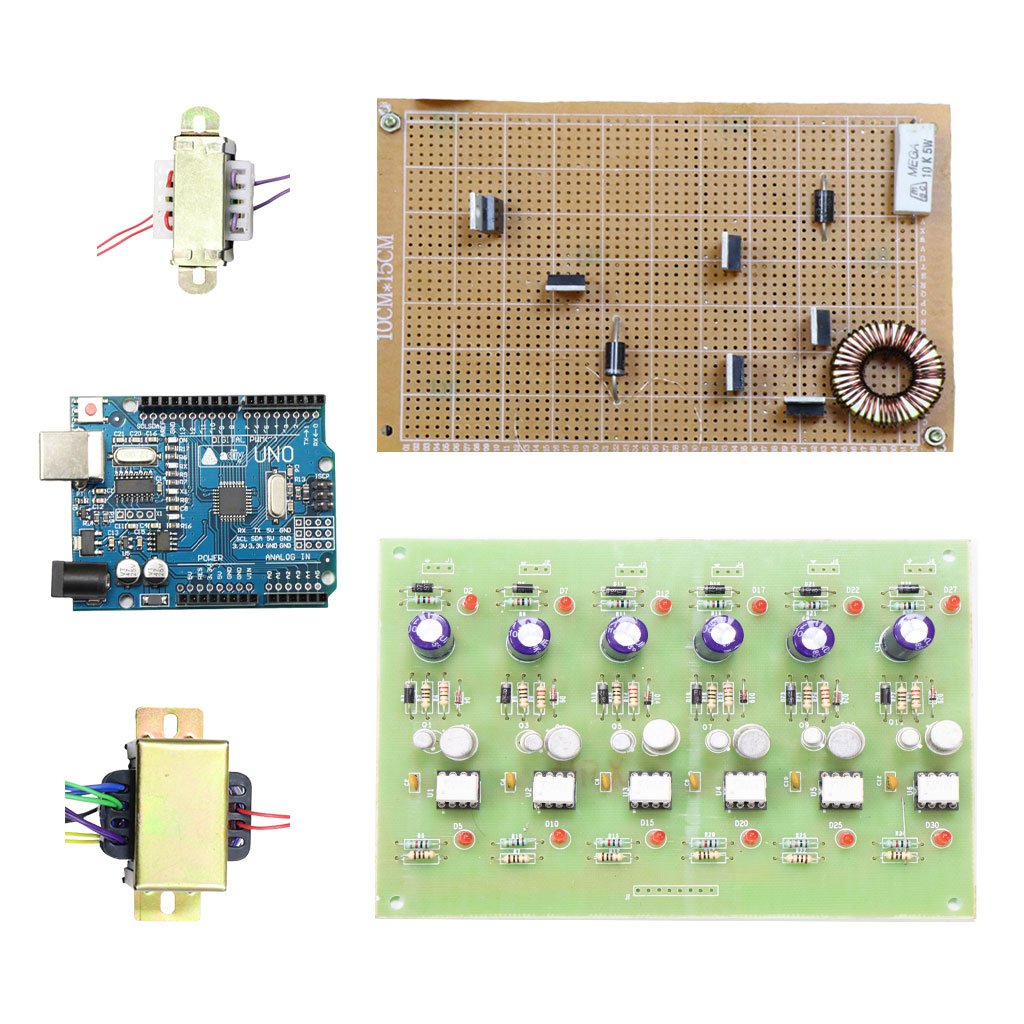
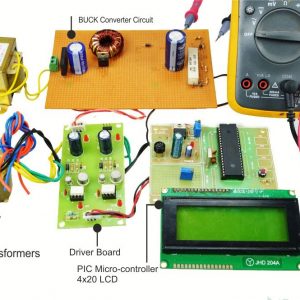
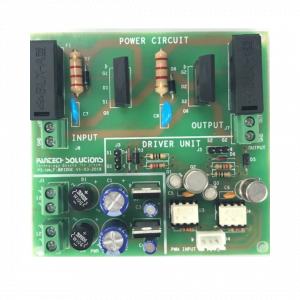
Hardware requirement
- Arduino microcontroller
- Circuit components
Capacitor? = 10uf
Inductor = 1? mh
Mosfet switches (irf250, irf840)
- Input supply
- Output measurement device
Software required
- Arduino ide
- Matlab (simulink)
Reference
- Kouro, m. Malinowski, k. Gopakumar, j. Pou, l. G. Franquelo, b. Wu and e. Al., “recent advances and industrial applications of multilevel converters,” ieee transactions on industrial electronics, vol. 57, no. 8, pp. 2553-2580, aug. 2010.
- Rodriguez, j.-s. Lai and f. Z. Peng, “multilevel inverters: a survey of topologies, controls, and applications,” ieee transactions on industrial electronics, vol. 49, no. 4, pp. 724-738, aug 2002.
- Z. Youssef, k. Woronowicz, k. Aditya, n. A. Azeez and s. S. Williamson, “design and development of an efficient multilevel dc/ac traction inverter for railway transportation electrification,” ieee transactions on power electronics, vol. 31, no. 4, pp. 3036-3042, april 2016.
- Nabae, i. Takahashi and h. Akagi, “a new neutral-point-clamped pwminverter,” ind.appl, vols. Ia-17, no. 5, p. 1981, 518?523.
- f.escalante, j.c.vannier and a.arzand?, “flying capacitor multilevel inverters and dtc motor drive applications,” ieeetrans.ind. Electron., vol. 49, no. 4, p. 809?815, 202.














































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Customer Reviews
There are no reviews yet.