Description
Health Care Monitoring using Raspberry Pi
OBJECTIVE
The objective of this system is to design a health care monitoring system that enables the implementation of an autonomous biomedical monitoring system
ABSTRACT
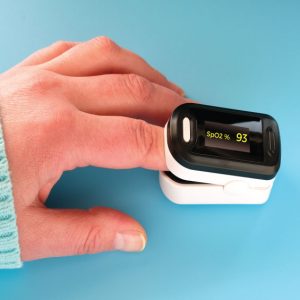
Internet of Things (IoT) is a new technological paradigm that can connect things from various fields through the Internet. For the IoT-connected healthcare applications, all the sensors are connected to Raspberry pi. Through this system, we can measure ECG, heartbeat, BP, and pulse. Through sensors, it is possible to measure all these values. All these analog sensors can be connected to Raspberry pi through ADC. These values are then used for detecting any critical situation. In the case of a critical situation, an alert can be given as a message. Also, it is possible to monitor a person’s health from any location in the world through the Thingspeak cloud. Data from sensors is uploaded to Thingspeak periodically without any interruption if the internet is available.
INTRODUCTION
Most humans live a busy life in which going to a doctor for weekly or even monthly checkups is an impossible task. Without monitoring your health it is not possible to know whether you are a healthy or sick person. This problem leads to the design of a product that monitors your health every day without going to a doctor. ECG is the most broadly used cardiovascular disease monitoring technique that measures the electrical activities of the heart. An ECG system is a non-invasive monitor for evaluating the heart’s electrical activity, measuring the regularity/rate of heartbeats, and identifying any damage to the heart. In this paper, a system is designed as a prototype for monitoring alerting based on the health of a person. This system is fully automated and little or no human help is needed. Any doctor can monitor this person from anywhere through the internet.
EXISTING SYSTEM
- Diagnosing with the help of a doctor
- Conventional devices that can only measure a particular parameter
- Devices that have to be connected invasively to get measurements
- No automated system exists
- Smartwatches are expensive and not specifically for healthcare
DISADVANTAGES
- This system also needs a doctor in case of an emergency
- The accuracy of output is less
- Costly system
PROPOSED SYSTEM
- In this system 24×7 human health, monitoring is designed and implemented
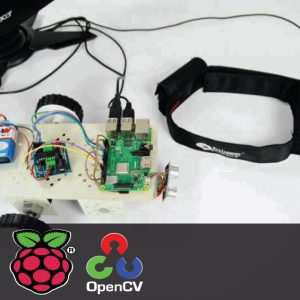
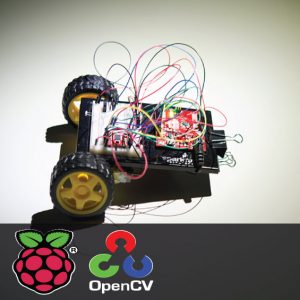
- In this system, the Raspberry pi board is used for collecting and processing all data
- Wireless devices have invaded the medical area with a wide range of capabilities.
- Monitor the patient details in a periodic interval is overhead using existing technologies.
- To overcome this we have changed recent wireless sensor technologies.
- Different sensors are used for measuring different parameters
- All this data is uploaded to thingspeak for remote analysis
ADVANTAGES
- A wide range of communication is available (IoT)
- Easy connectivity between modules
- Accuracy of output is increased
- Easy to implement in real-time
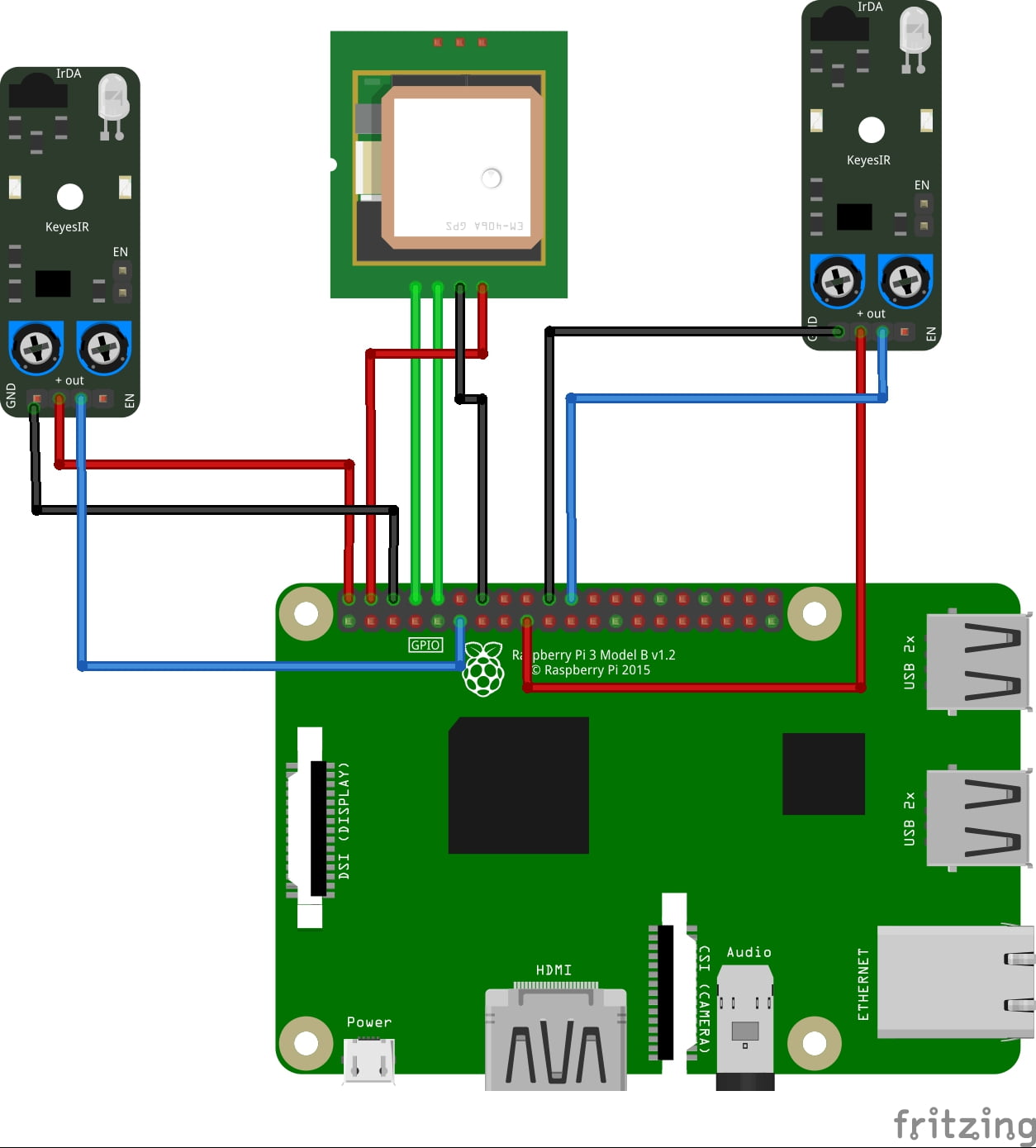
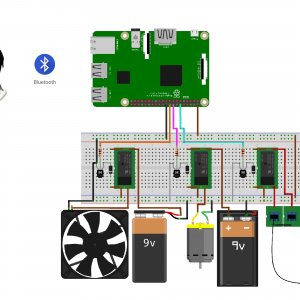
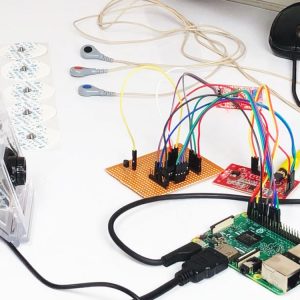
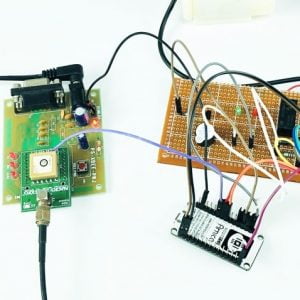
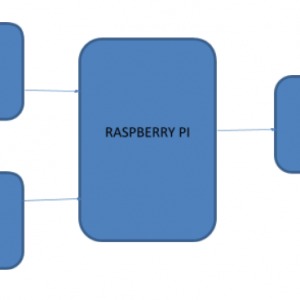
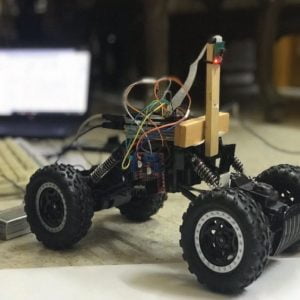
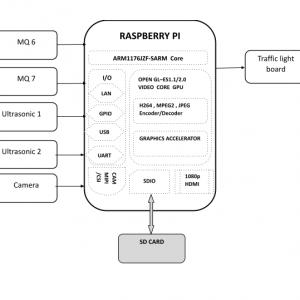
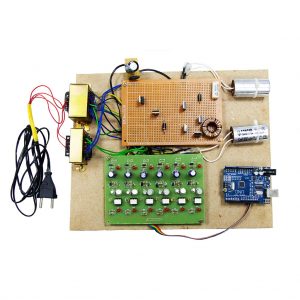
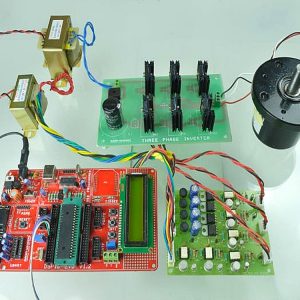
BLOCK DIAGRAM
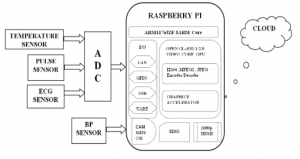
BLOCK DIAGRAM EXPLANATION
- The sensors that are mentioned above in the block diagram act as an input device
- They give live readings to the Raspberry pi and ADC for converting analog values to digital values
- Raspberry pi receives the input from sensors
- Raspberry pi sends output to the cloud through the MQTT protocol
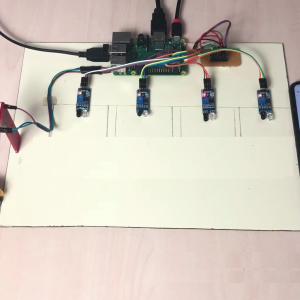
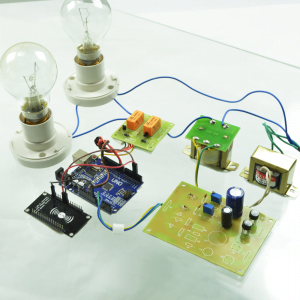
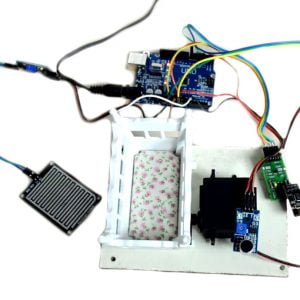
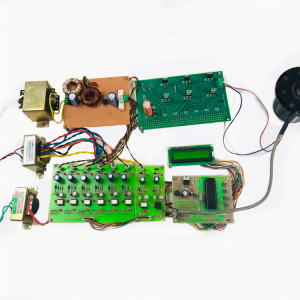
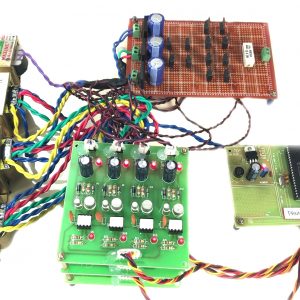
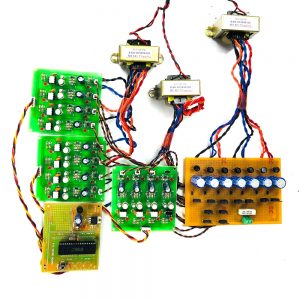
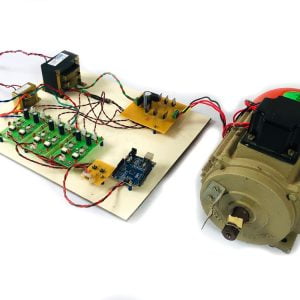
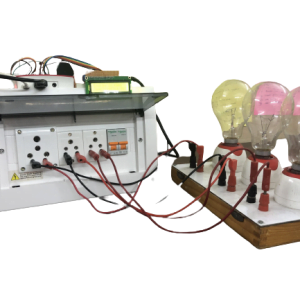
HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS
- Raspberry pi
- ECG sensor
- Blood pressure sensor
- Pulse Sensor
- Temperature sensor
- ADC
SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS
- Programming platform: Python IDE
- Raspberry pi OS: Raspbian stretch
- Programming language: Python
REFERENCE
- M. Hong, Z. Yajun and H. Xiaoping, “Portable ECG measurement device based on MSP430 MCU,” in Proc. BMEI, 2008, pp. 667–671.
- N. Ebrahim, M. J. Deen, and T. Mondal, “A wireless wearable ECG sensor for long-term applications,” IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 36–43, Jan. 2012.
- J. M. Cano-Garcia, E. Gonzalez-Parada, V. Alarcon-Collantes and E. Casilari-Perez, “A PDA-based portable wireless ECG monitor for medical personal area networks,” in Proc. MELECON, 2006, pp. 713–716.
- T. K. L. Hui, R. S. Sherratt, and D. Diaz Sanchez, “Major requirements for building Smart Homes in Smart Cities based on Internet of Things technologies,” Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 76, pp. 358– 369, Nov. 2017.



































































































































































































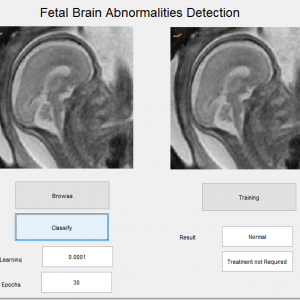








































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Customer Reviews
There are no reviews yet.