Description
Healthcare Chatbot
Abstract: Healthcare Chatbot – Automatized medical chatbots are conversationally built with technology in mind with having the potential to reduce efforts to healthcare costs and improve access to medical services and knowledge.
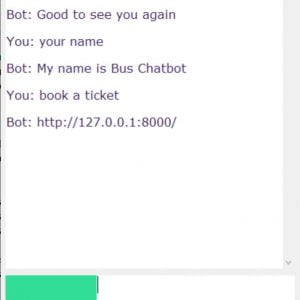
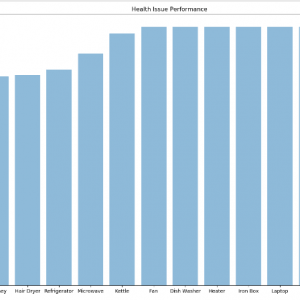
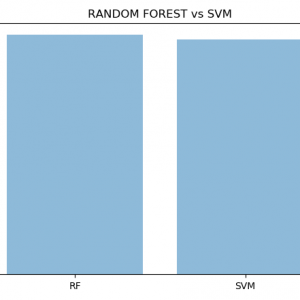
We built a diagnosis bot that engages patients in the conversation for their medical queries and problems to provide an individualized diagnosis based on their diagnosed manifestation and profile. Our chatbot system is qualified to identify symptoms from user inputs with a standard precision of 65%. Using these extracted diagnosed symptoms correct symptoms were identified with a recall of 65% and a precision of 71%. Finally, the chatbot returned the expected diagnosis for further operations. This determines that a medical chatbot can provide a somewhat accurate diagnosis to patients with simple symptom analysis and a conversational approach, this suggests that an effective spoken language medical bot could be viable. Moreover, the relative effectiveness of this bot indicates that more proceeds automated medical products may flourish to serve a bigger role in healthcare.
Introduction:
Healthcare Chatbot – An automatized medical chatbot is a system with human interaction using natural language diagnosis to provide medical aid.
The vast amount of information that is available on the internet allows chatbots to provide accurate and systematic statistics based on the user’s demand and requisite. Chatbots are used in domains like Customer Support and Services, Virtual Assistance, Online Trainers, and Online Reservations and also for general conversations. We built a diagnosis bot that engages patients and explains their state using natural language. The bot inquires for relevant particulars, e.g., name, age, etc., and appeals for symptoms. Our bot can withdraw patterns from messages using AIML (Artificial Intelligence Mark-up Language) based on XML (Extensible Mark-up Language) to strengthen AI (Artificial Intelligence) applications [1]. The structure asks progressively more specific questions in order to obtain a good diagnosis. The three primary components of our system are recognition and drawing out of symptoms from the discussion with the user.x accurate detection of extracted symptoms to documented symptoms in the database. x developing recognition as well as referring the patient to the most appropriate specialist if necessary. The system was also compared to the popular chatbots available. Our motive is to show that the proposed medical Chatbot could be a better alternative to many already existing bots in the domain of medical science.
Objective:
The system not only diagnosis the patients but can also detect the disease or illness of an individual by the symptoms provided by the individual. The process can be systematically recurrent with automated regression tests to shield the stability of the procedure.
Problem Statement:
All the activities inside a hospital are carried out manually. The patients need to register and the doctors can view the patient details and provide the necessary treatment based on the symptoms of the patient. All this requires a lot of human effort and time and the performance is not good. Moreover, it is prone to a lot of errors. To overcome these shortcomings, an automatized medical chatbot has been designed. The chatbot will listen to user queries, converts speech to text, and provide them with relevant answers. Chatbot keeps track of the patient’s status and provides suitable answers in relation to their diseases.
Existing System:
The system is based on the conversational data that the user provides during the conversation. The idea behind this is to focus on the preliminary symptoms and the problems that the user may be experiencing. After the automated medical chatbot has collected enough data from the initial conversation, it now forwards the conversation by asking questions to the user and trying to review diseases by converting the input data into queries and executing it.
Disadvantages:
- Complex interface
- Inability to Understand
- Time-consuming
- Increase installation cost
Proposed System:
- Introducing the machine learning-based chatbot
- This chat-bot will base on NLP
Advantages:
- less time spent commuting to the doctor’s office
- less money spent on unnecessary treatments and tests
- easy access to the doctor at the push of a button
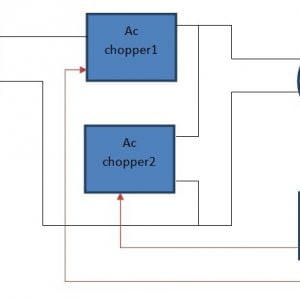
Block Diagram:
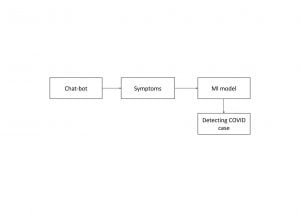
- Healthcare Chatbot
Modules
- DATA COLLECTION
- DATA PRE-PROCESSING
- FEATURE EXTRACTION
- EVALUATION MODEL
Hardware & Software Requirement
Software Requirements:
- Operating System: Windows 7, 8, and 10 (32 and 64 bit)
- Front End: Python
- Packages: NumPy, Pandas, itertools, matplotlib, sklearn, Keras , TensorFlow
- Back End: DataSet
Hardware Requirements:
- Processor – Dual Core
- Speed – 3.1 GHz
- RAM – 4 GB
- Hard Disk – 200 GB
Conclusion
We advanced in developing an automatized medical chatbot that layout personalized recognition based on symptoms this bot utilizes an external, closed-source recognition engine, so in order to upgrade the functionality of the diagnosis, it may be obligatory to develop an engine from scrape or find discover another asset that holdup expansion that can be useful in the long run.
REFERENCES
[1] .Comendador, B. E., Francisco, B. M., Medenilla, J. S., Nacion, S. M., & Serac, T. B. (2015). Pharmabot: A Pediatric Generic Medicine Consultant Chatbot. Journal of Automation and Control Engineering, 3(2), 137-140. DOI:10.12720/joace.3.2.137-140.
[2] .Kazi, Hameedullah & S. Chowdhry, B & Memon, Zeesha. (2012). MedChatBot: An UMLS-based Chatbot for Medical Students. International Journal of Computer Applications. 55. 1-5. 10.5120/8844-2886.
[3] .Shawar, BA and Atwell, E (2002) A comparison between Alice and Elizabeth Chatbot systems. The University of Leeds, School of Computing research report 2002.19.
[4]. Abu Shawar, BA and Atwell, ES (2004) An Arabic Chatbot giving answers from the Qur’an. In: Bel, B, and Marlien, I, (eds.) Proceedings of TALN04: XI Conference sur le Traitement Automatique des Langues Naturelles. TALN04: XI Conference sur le Traitement Automatique des Langues Naturelles, 19-22 April 2004, Fez, Morocco. ATALA, 197 – 202. ISBN2-9518233-5-5.














































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Customer Reviews
There are no reviews yet.