Description
BCI Home Automation using Arduino
Abstract
BCI Home Automation – A brain-computer interface (BCI) is a new communication channel between the human brain and a digital computer. The ambitious goal of a BCI is finally the restoration of movements, communication, and environmental control for handicapped people. An electroencephalogram (EEG) based brain-computer interface was connected with a Virtual Reality system in order to control a smart home application. It offers an alternative to natural communication and control. It is an artificial system that bypasses the body’s normal efficient pathways, which are the neuromuscular output channels. BCI Home Automation using Arduino
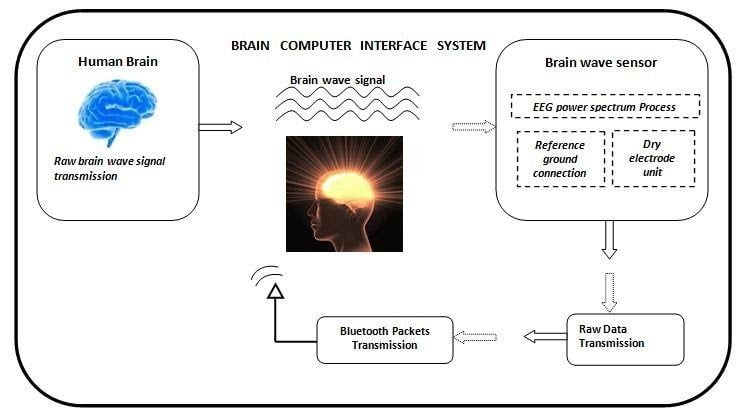
Different brain states are the result of different patterns of neural interaction. These patterns lead to waves characterized by different amplitudes and frequencies. This neural interaction is done with multiple neurons. Every interaction between neurons creates a minuscule electrical discharge. This project deals with the signals from the brain. Different brain states are the result of different patterns of neural interaction. These patterns lead to waves characterized by different amplitudes and frequencies. The signal generated by the brain was received by the brain sensor and it will divide into packets and the packet data is transmitted to a wireless medium (blue tooth). the wave measuring unit will receive the brain wave raw data and it will convert it into the signal using the MATLAB GUI platform. Then the instructions will be sent to the home section to operate the modules (bulb, fan). The project operated with human brain assumption and the ON/OFF condition of the home appliance is based on changing the muscle movement with blinking. BCI Home Automation using Arduino
BCI Home Automation using Arduino
Introduction
BCI Home Automation -A Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) is a new communication channel to capture human thoughts. By using BCI it has become possible to link brain activity to the operation of computers and devices and hence creating a direct communication channel between mind and machine. The BCI technology can be used by disabled people to improve their independence and maximize their capabilities at home. This project is designed to help disabled people to control the appliance with an increased inaccuracy.
This paper presents a new architecture for home device control systems via thoughts. Such a system will be useful for people who are suffering from paralysis or a similar condition, who have limited movement. For disabled people, controlling a household device such as light, fan air-conditioning, etc, will be dif? cult without any assistance.
Existing system
- Voice command is the most used technology for home Automation
- It can’t be used in a noisy environment
- The system accuracy is high in a closed environment. But actual Accuracy in daily life is very low.?
- The Voice system is irritating and ineffective
Proposed system
The proposed approach helps people physically disabled to control home appliances using Electroencephalogram signals (EEG). For home automation, identifying and locating the user and calculating their viewing angle are needed. The proposed approach has mainly four modules and is given below.?
- Image acquisition and feature extraction?
- Calculating the user’s viewing angle?
- Capturing and identifying the EEG signal?
- Device control
Advantage
- Allow paralyzed people to control prosthetic limbs with their limbs
- Transmit visual image to the mind of a blind person
- Transmit auditory data to the mind of a deaf person
- Allow persons to control home automation with their mind
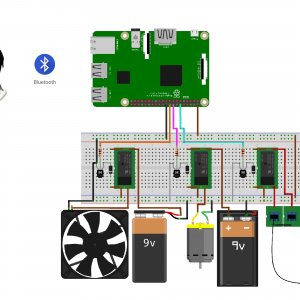
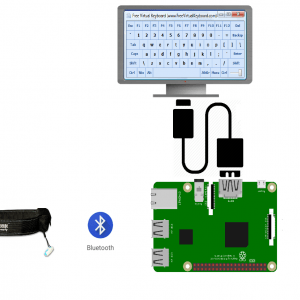
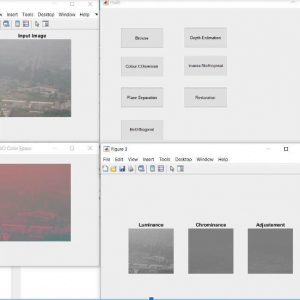
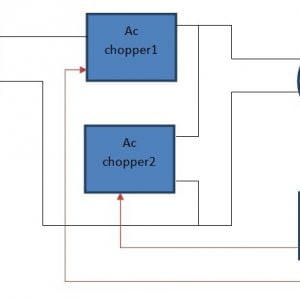
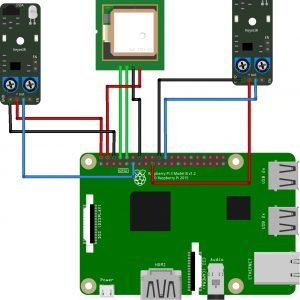
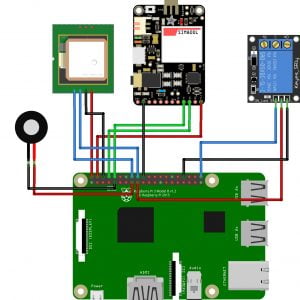
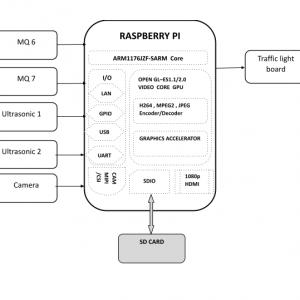
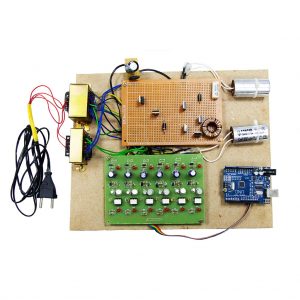
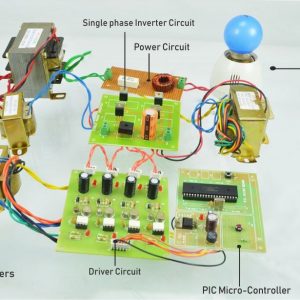
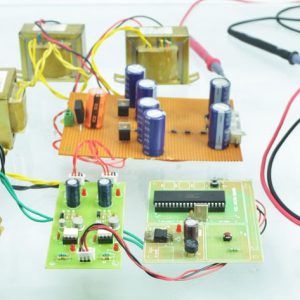
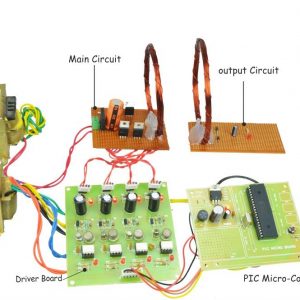
Block Diagram
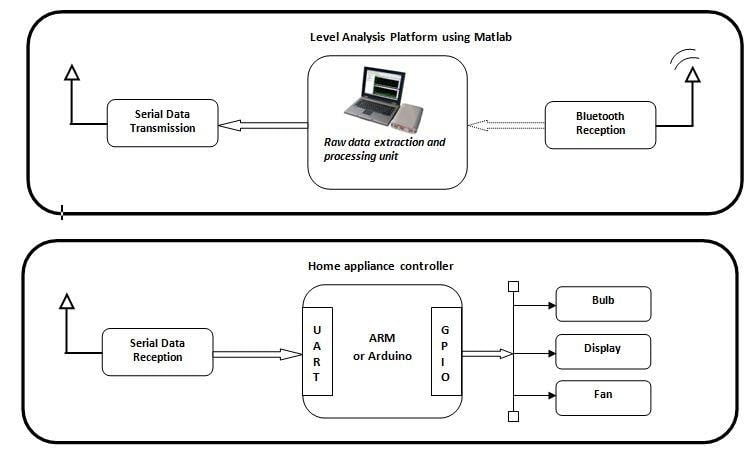
Block diagram explanations:
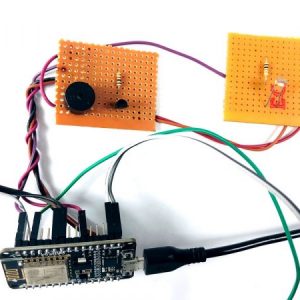
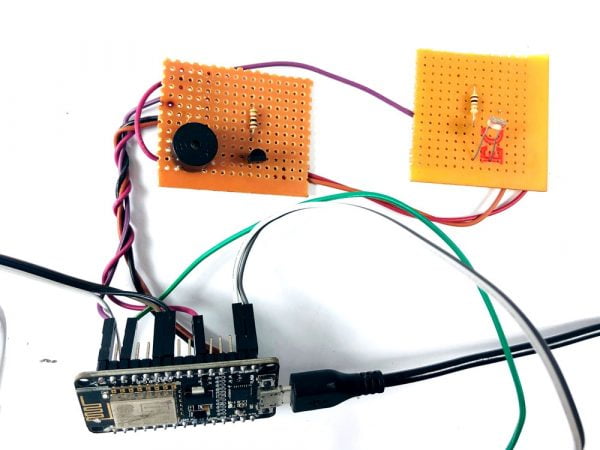
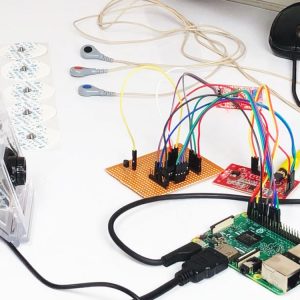
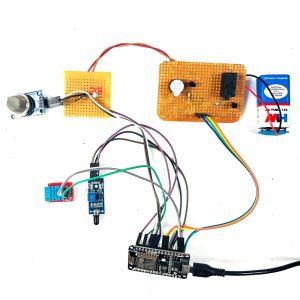
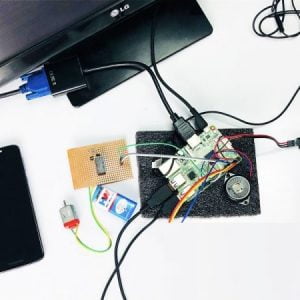
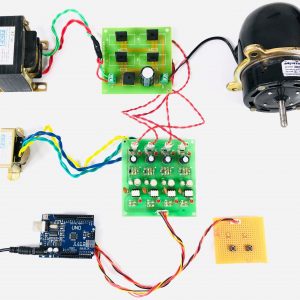
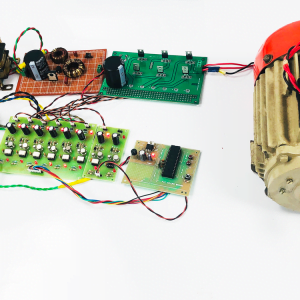
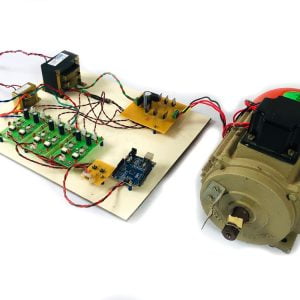
BCI system captures the electrical signals from the forehead position. The electrodes will then send the signals to the amplifier and filter circuit wherein the signal is amplified and unwanted noise and signals are filtered out . The analog signals are then converted into digital signals by the inbuilt ADC of Arduino. Since the electrical signals are taken from the forehead position near the eyes, they contain data regarding eye movement. Thus we obtain the eye blink count from the obtained electrical signal. The microcontroller process the signals based on the following logic:?
- Whenever we blink, EEG waves will encounter a peak.?
- This peak value is set as the threshold value.?
- If weblink, the output of the ADC goes beyond the threshold value, the Arduino counts it as a blink.?
- The moment we weblink, the timer of the microcontroller will start.
- If we weblink a certain number of times in a certain interval of time, the microcontroller will enable the relay switches.?
- Depending on which relay switch is provided with the control signal, the respective device turns on.?
- The number of blinks and the interval can be decided by the user.
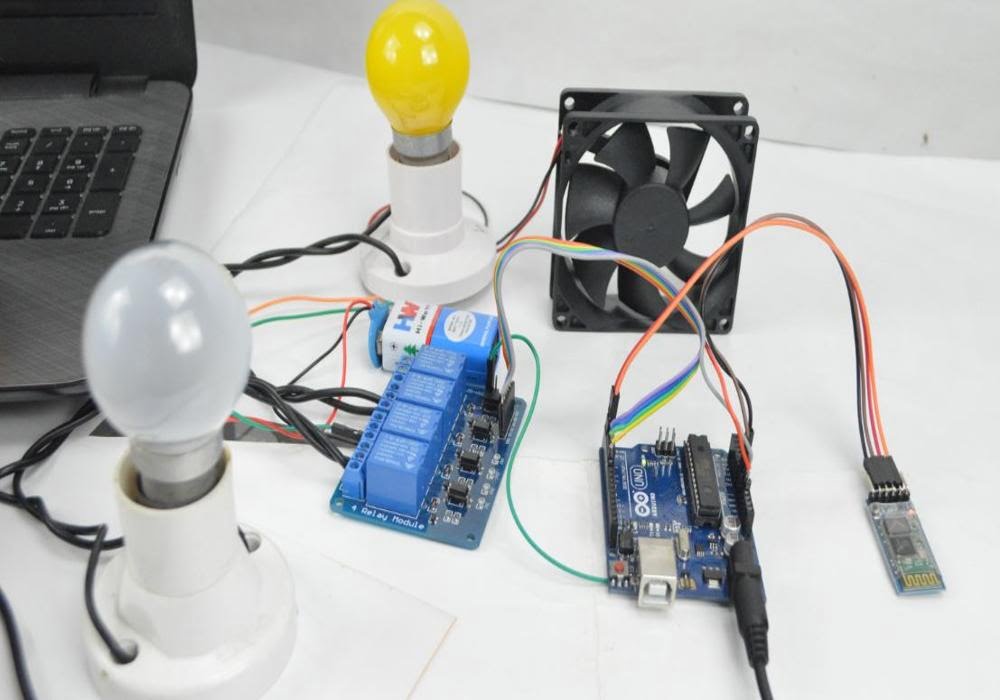
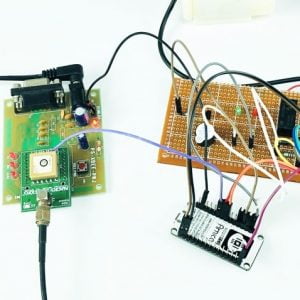
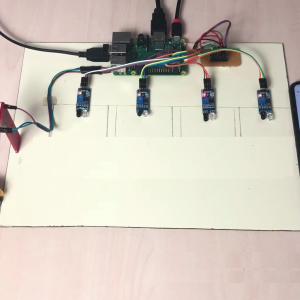
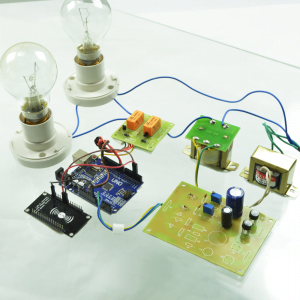
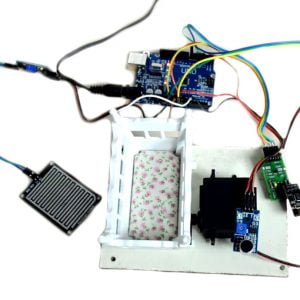
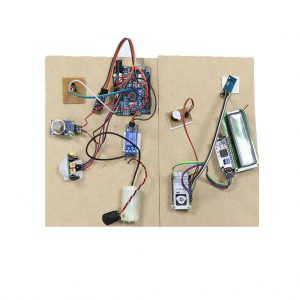
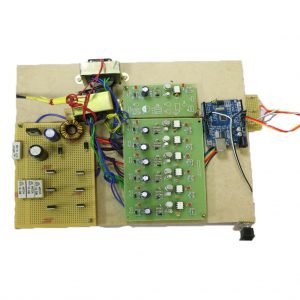
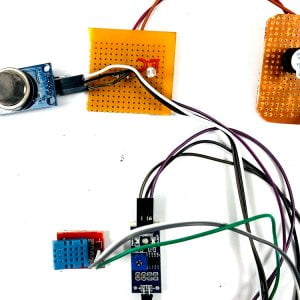
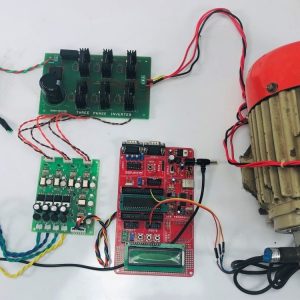
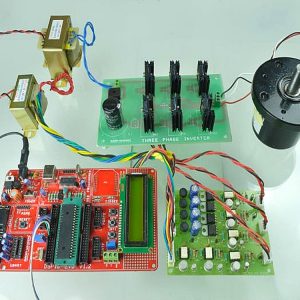
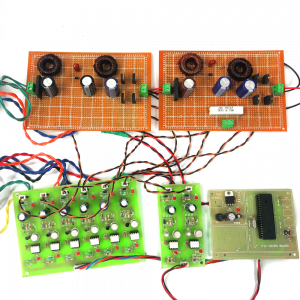
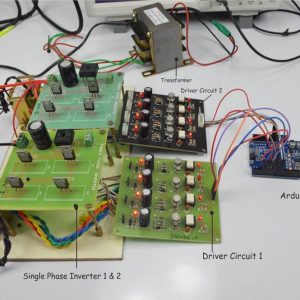
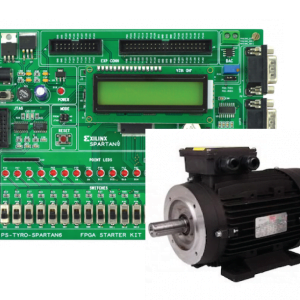
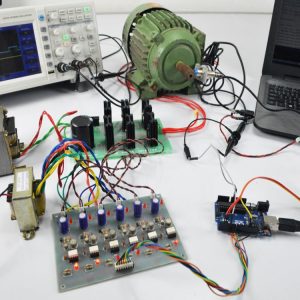
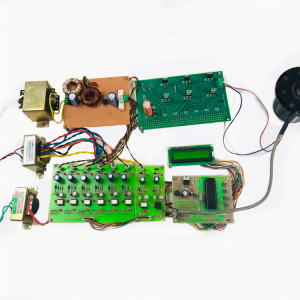
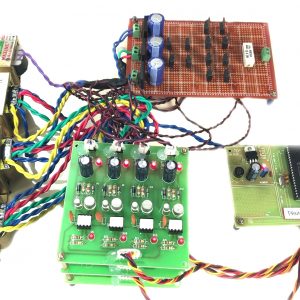
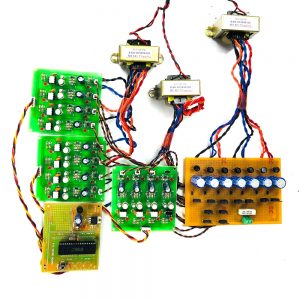
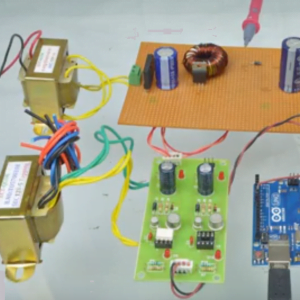
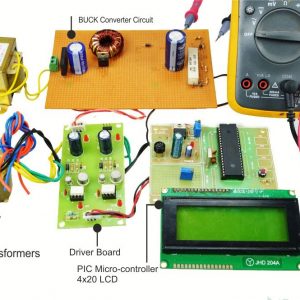
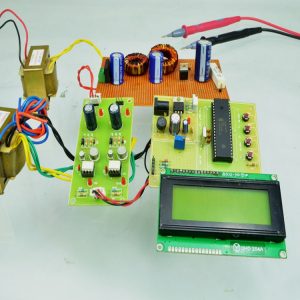
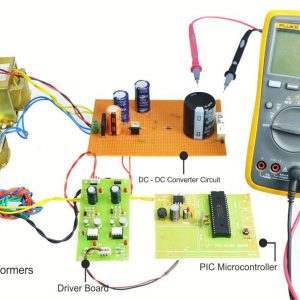
HARDWARE REQUIRED
- Mind Wave Mobile Or Brainsense
- Laptop or Pc
- Arduino Uno/Mega
- Bluetooth Module ( HC-05 )
- USB Cable for Arduino
- Bluetooth dongle, if your pc does not have internal Bluetooth
- Relay Module
- Home appliances

Zeta Converter Using Arduino 2 
leap motion
SOFTWARE REQUIRED
- Matlab 2013b (32 bit)
- Arduino
REFERENCES?
[1] X. Gao, D. Xu, M. Cheng, and S. Gao,?A BCI-based environmental controller for the motion-disabled,? IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 11, pp. 137? 140, June 2003.?
[2] C. Zickler, V. Di Donna, V. Kaiser, A. Al-Khodairy, S. Kleih, A. K?ubler, M. Malavasi, D. Mattia, S. Mongardi, C. Neuper, et al., ?By applications for people with disabilities: de?ning user needs and user requirements,? Assistive technology from adapted equipment to inclusive environments, AAATE, vol. 25, pp. 185? 189, 2009.?
[3] S. P. Levine, J. E. Huggins, S. L. Bement, R. K. Kushwaha, L. A. Schuh, M. M. Rohde, E. A. Passaro, D. A. Ross, K. V. Elisevich, and B. J. Smith,?A direct brain interface based on event-related potentials,? IEEE Transactions on Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 8, pp. 180? 185, Jun 2000.?
[4] J. J. Vidal,?Real-time detection of brain events in EEG,? Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 65, pp. 633? 641, May 1977.?
[5] J. J. Daly and J. E. Huggins,?Brain-computer interface: current and emerging rehabilitation applications,? Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation, vol. 96, no. 3, pp. S1?S7, 2015.?
[6] F. Miralles, E. Vargiu, X. Rafael-Palou, M. Sol`a, S. Dauwalder, C. Guger, C. Hinterm?uller, A. Espinosa, H. Lowish, S. Martin, et al., ?Brain? computer interfaces on track to home: results of the evaluation at disabled end-users homes and lessons learned,? Frontiers in ICT, vol. 2, p. 25, 2015.














































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Customer Reviews
There are no reviews yet.