Description
LoRa- based Wireless Sensors for Smart Environment and IoT Applications
This paper proposes a monitoring system that has a number of nodes for monitoring parameters such as co level, poisonous gas, temperature, and humidity. A node is designed for data acquisition and another one is designed for data collecting for further analysis. We can create any number of data acquisition nodes with a single collecting node. For interconnecting all these nodes it is possible to have WiFi-based IoT as existing. This has a disadvantage in that the WiFi modem needs to connect to a wider network, so proper working of the whole system is dependent on the availability of this network. Here we eliminate this problem by introducing a LoRa which means long-range. Using LoRa we can make our own interconnected IoT applications. Although many techniques exist to transfer data from the widely distributed sensors that make up the (IoT) (e.g., using 3G/4G networks or cables), these methods are associated with prohibitively high costs, making them impractical for real-life applications. Recently, several emerging wireless technologies have been proposed to provide long-range communication for IoT sensors. Among these, LoRa has been examined for long-range performance.LoRa-based Wireless Sensors for Smart Environment and IoT Applications
LoRa-based Wireless Sensors for Smart Environment
INTRODUCTION
Lora (Long Range) is a spread spectrum modulation technique that provides a significantly longer-range transfer of data and information with a lower transfer rate than the competing technologies. LoRaWAN is an LPWAN protocol that is based on LoRa modulation and was intended to remotely connect battery-operated things to the internet in local, regional, or worldwide networks. LoRaWAN protocol uses the unlicensed radio spectrum in the ISM band, such as 433MHz, 868MHz, and 915MHz. LoRaWAN network is implemented by using a star network topology and the structure of the network architecture can be divided into two parts, the back-end and front-end part. The back-end part is the network server which is used to store the information sent by the sensors while the front-end consists of end devices and a gateway, the gateway is the intermediate device that forwards packets coming from the end devices to the network server. LoRaWAN network is implemented by using a star network topology and the structure of the network architecture can be divided into two parts, the back-end and front-end part.
LoRa based Wireless Sensors for Smart Environment and IoT Applications
EXISTING SYSTEM
- Monitoring systems without any interconnectivity
- Systems that use IoT based on WiFi network
- Systems based on RF communication
DISADVANTAGES
- This system always needs internet connectivity
- If the internet is slow it takes some delay to update in the cloud
- The accuracy of output is less
- Communication range is low in the existing system
PROPOSED SYSTEM
- Monitoring surroundings parameters using sensors
- Multimode monitoring system
- LoRa – based long-range communication
- Multiple sensor nodes connected to a single monitoring node
ADVANTAGES
- It is a cost-efficient system
- Accuracy of output is increased
- Longe range communication is implemented
- Using IoT in this project is the main advantage, so we can get the status of the system at any place in the world
LoRa-based Wireless Sensors for Smart Environment and IoT Applications
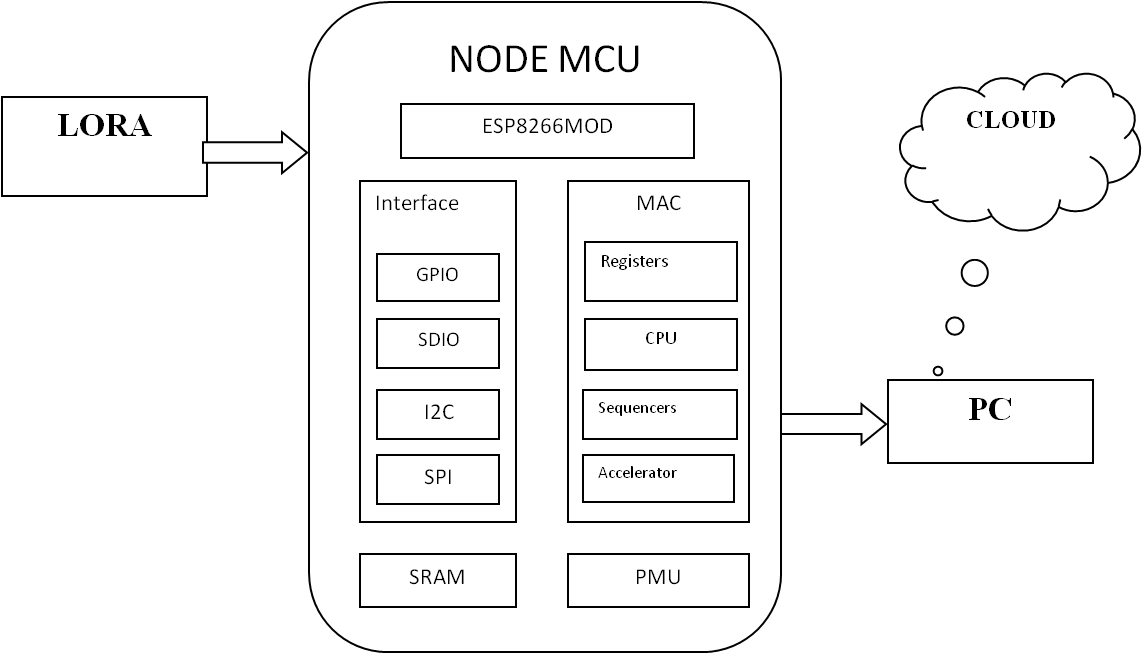
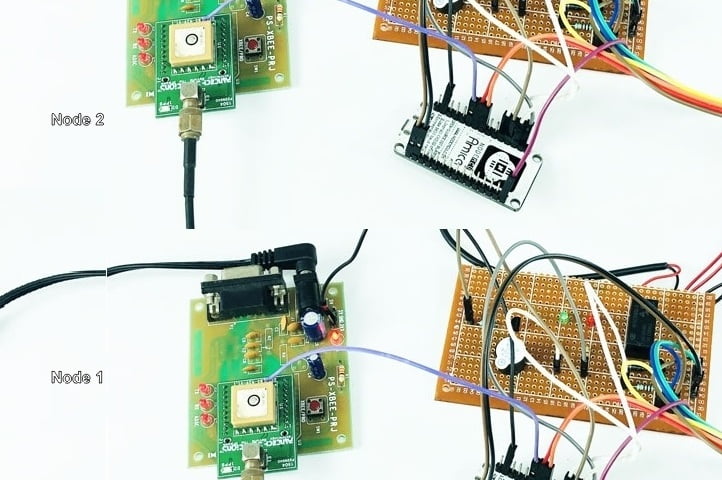
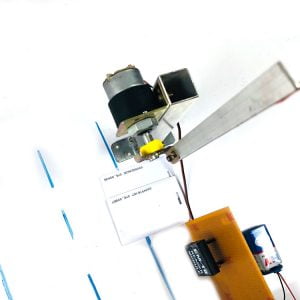
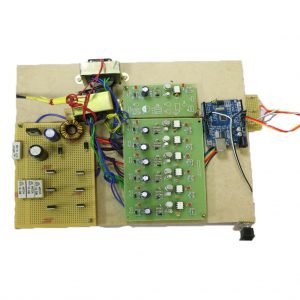
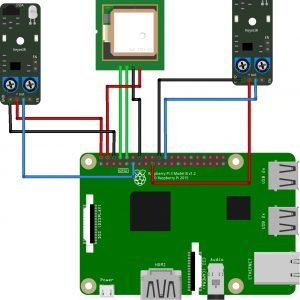
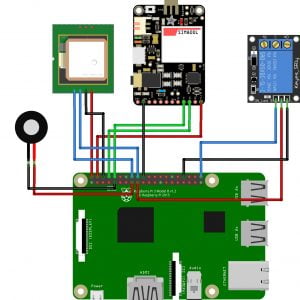
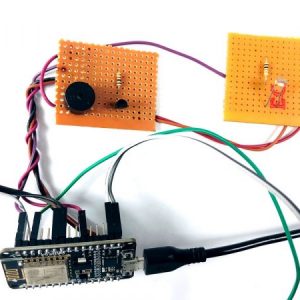
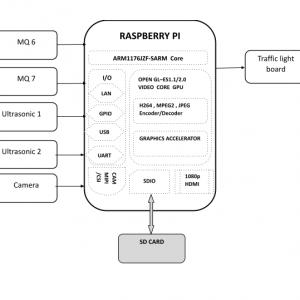
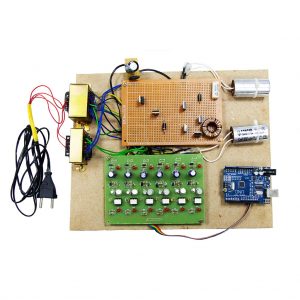
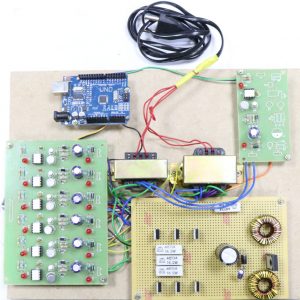
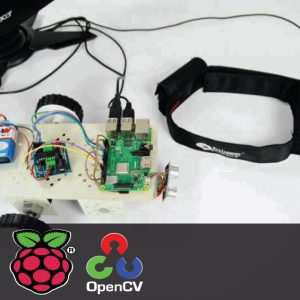
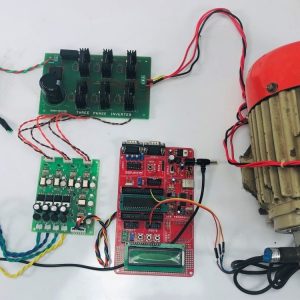
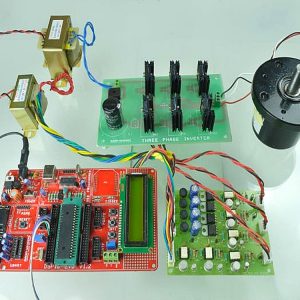
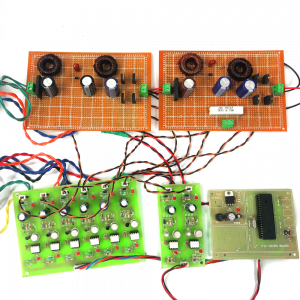
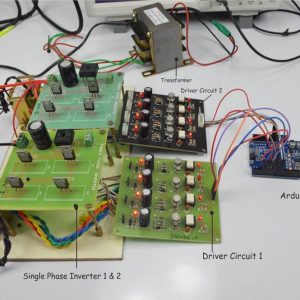
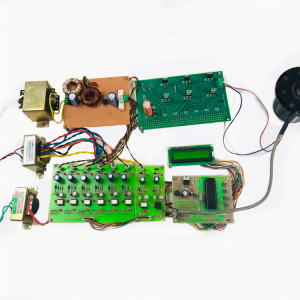
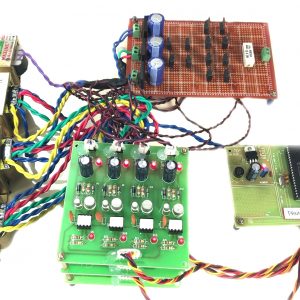
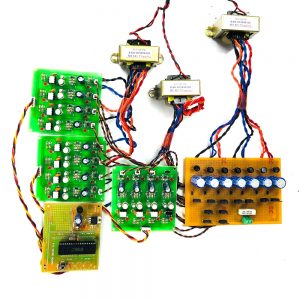
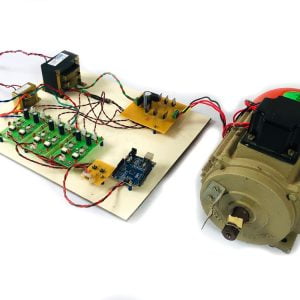
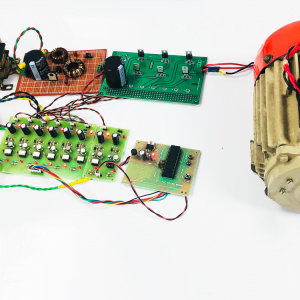
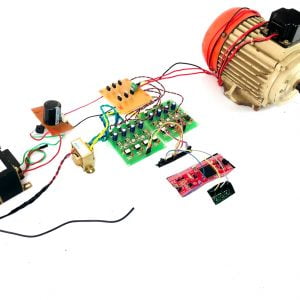
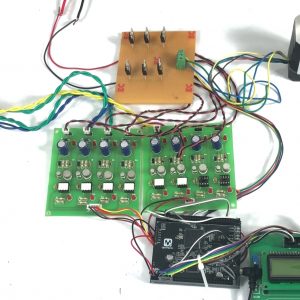
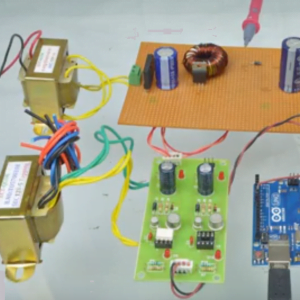
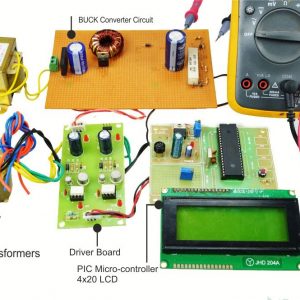
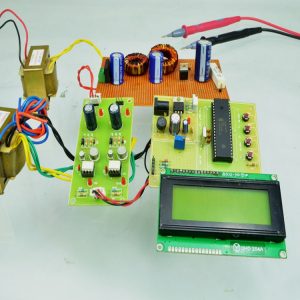
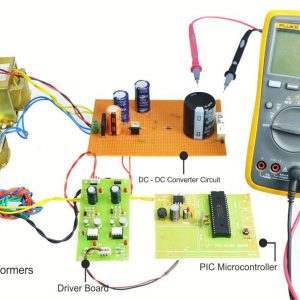
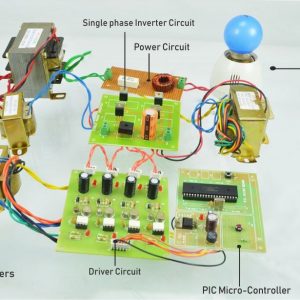
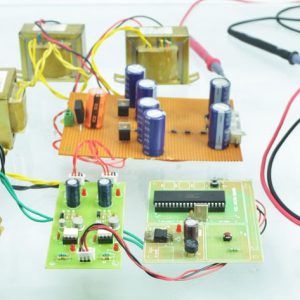
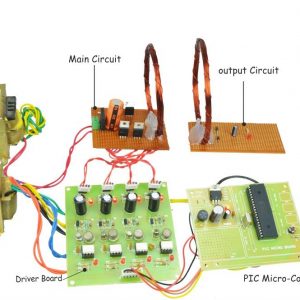
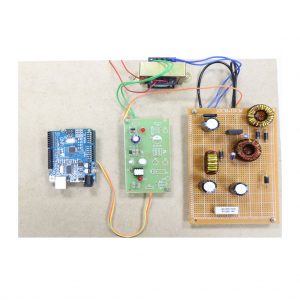
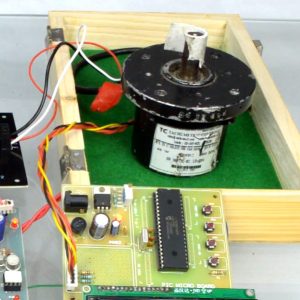
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
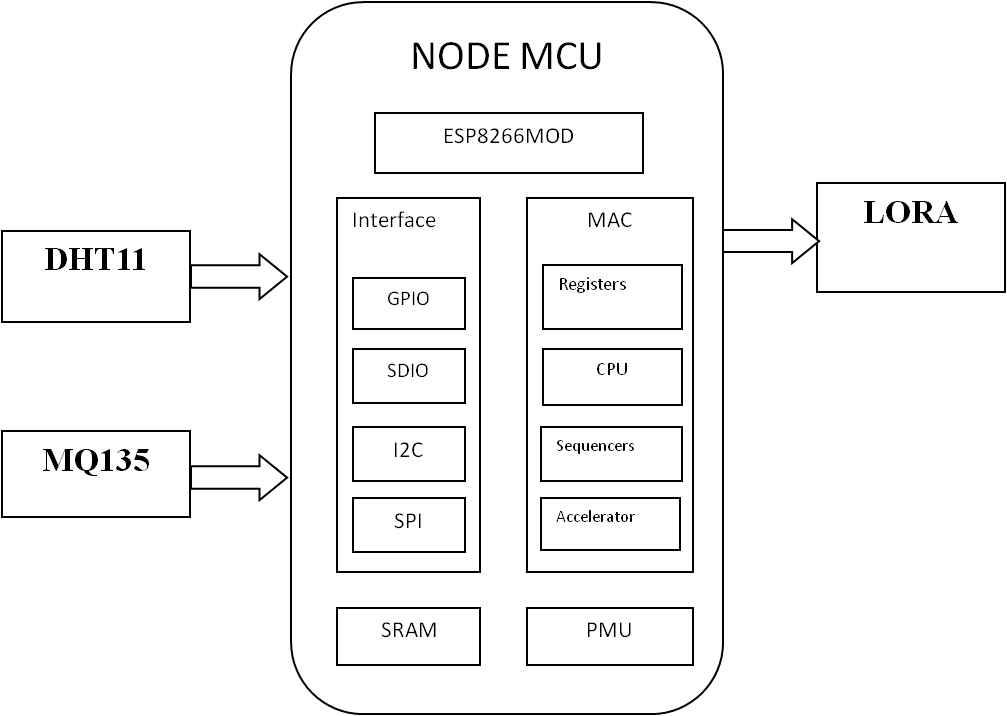
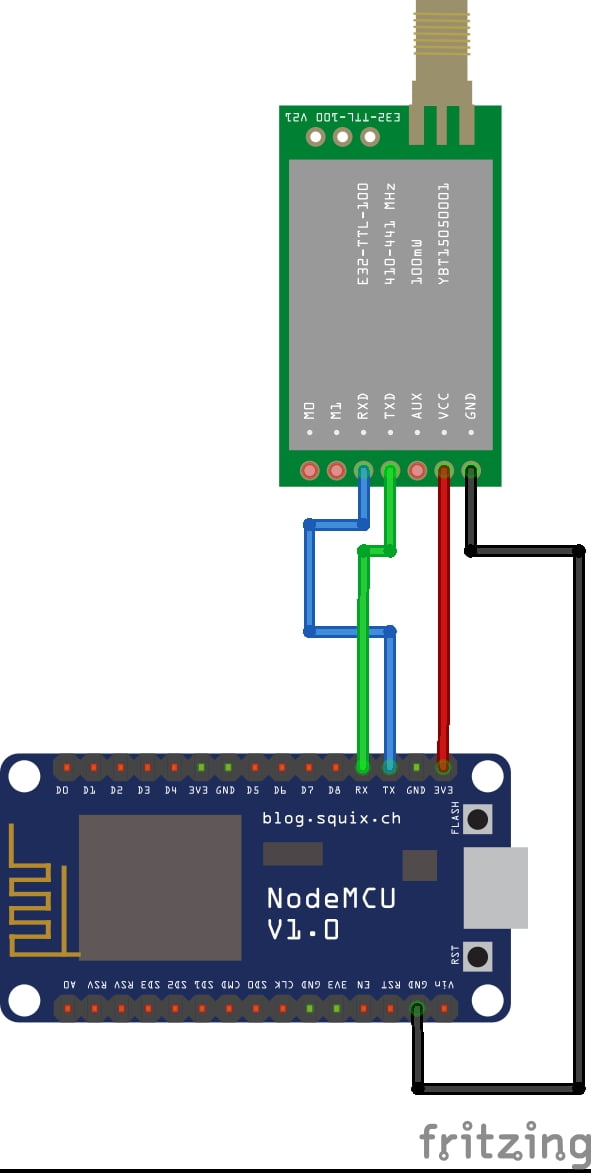
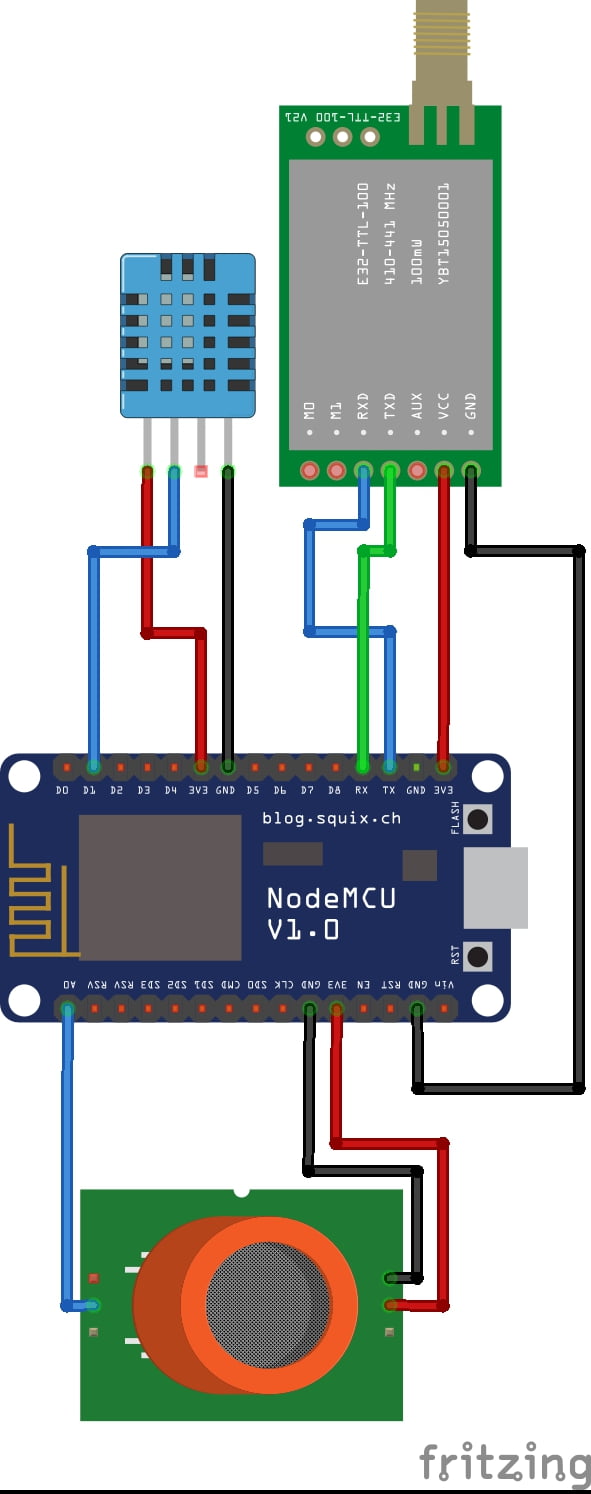
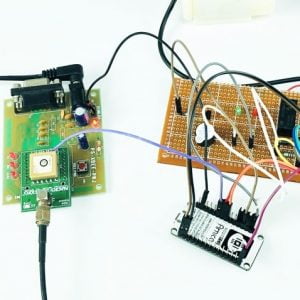
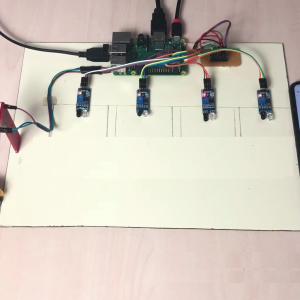
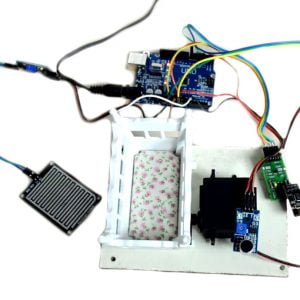
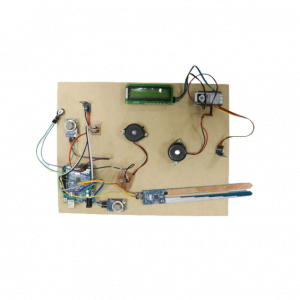
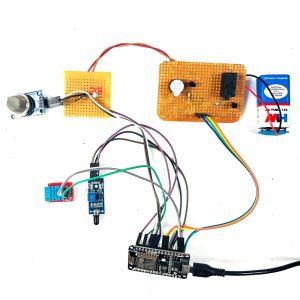
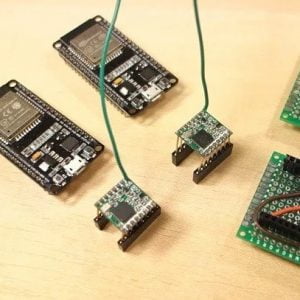
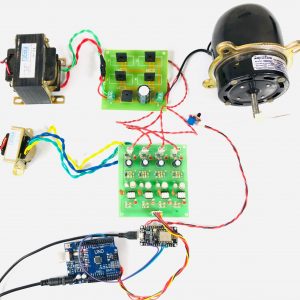
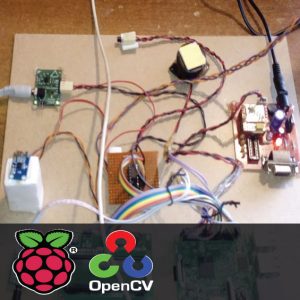
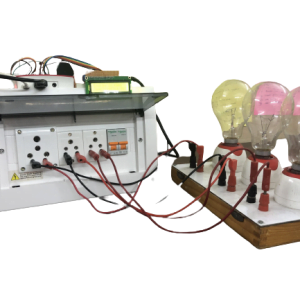
DATA COLLECTING NODE:
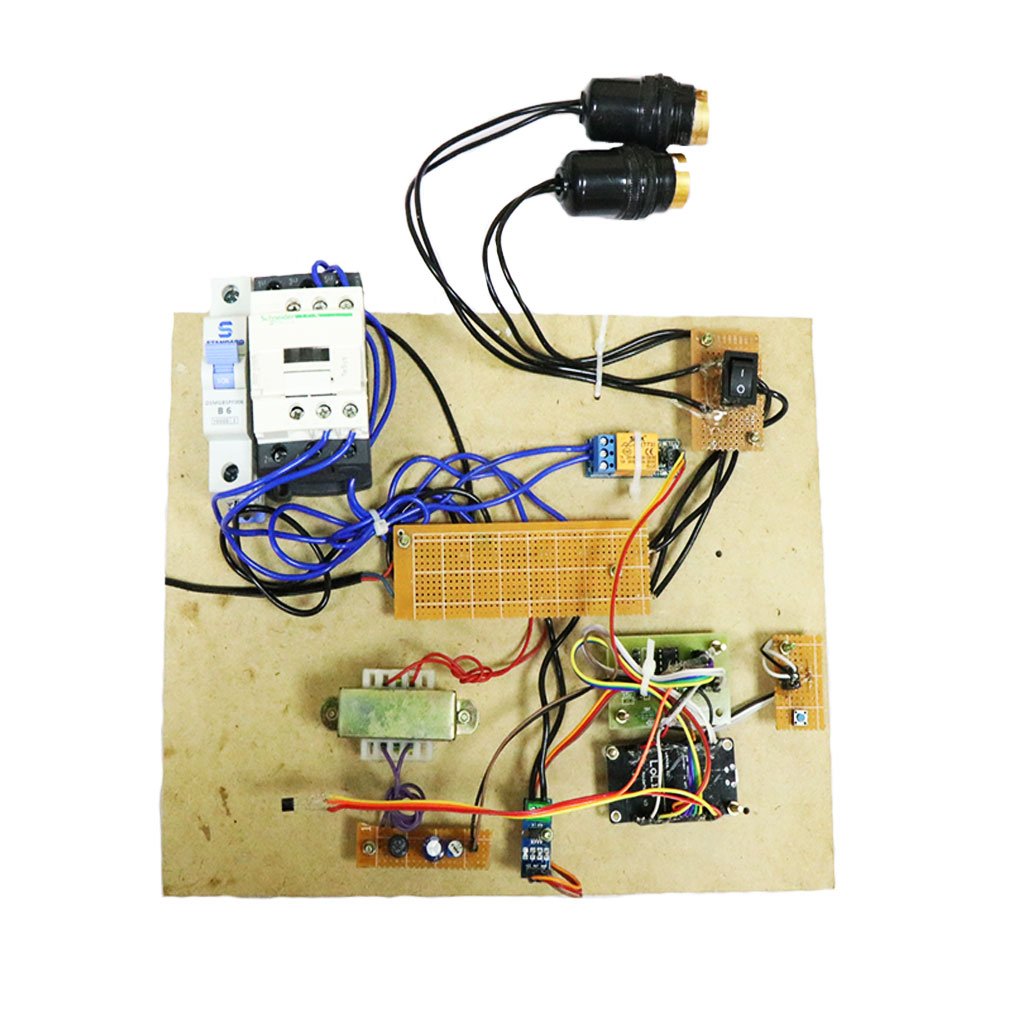
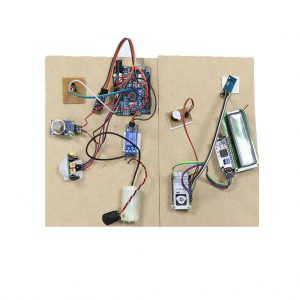
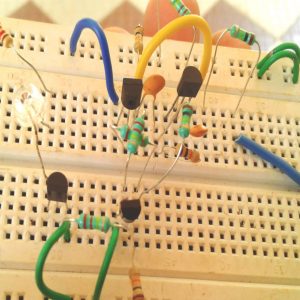
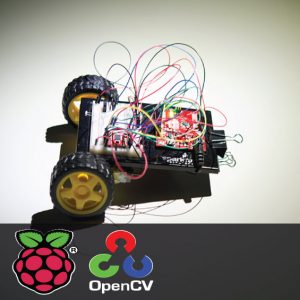
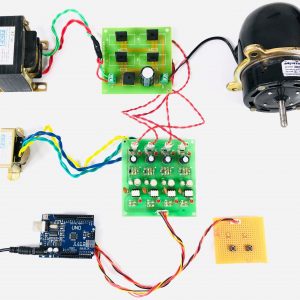
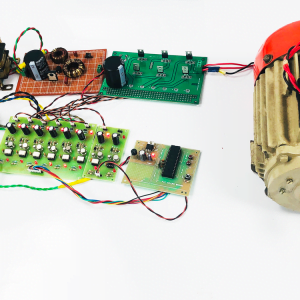
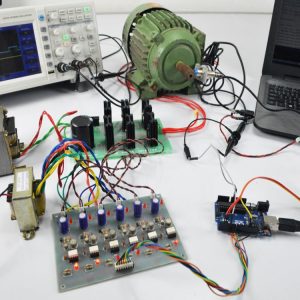
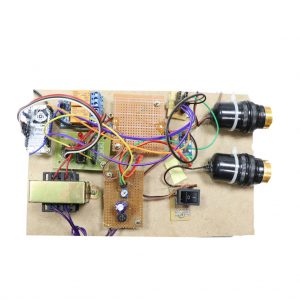
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
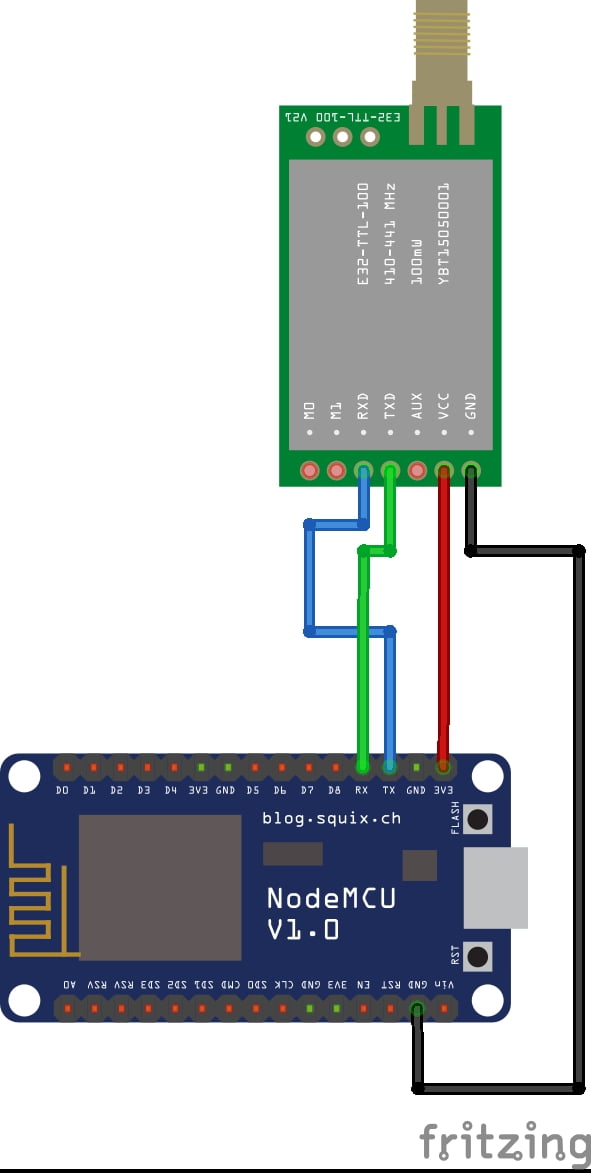
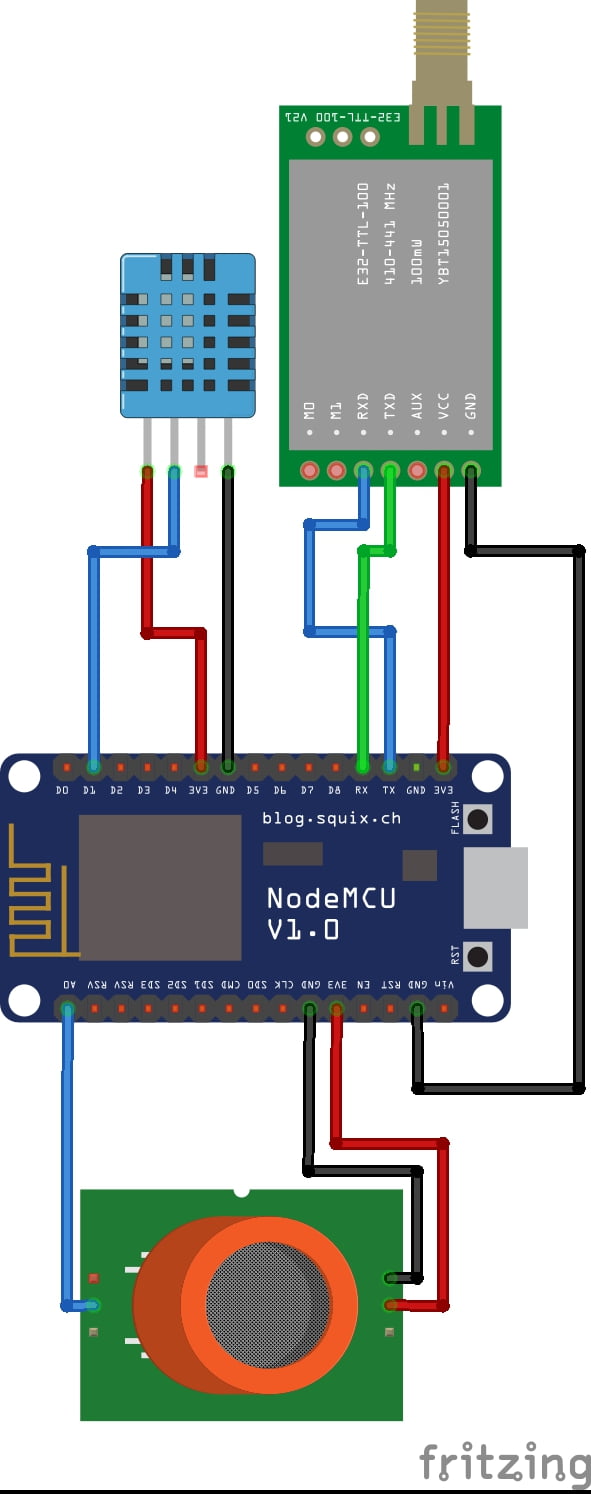
BLOCK DIAGRAM EXPLANATION:
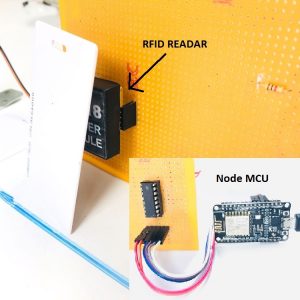
- Here Node MCU is the central part
- We can use any type of microcontroller or SoC depending on the application
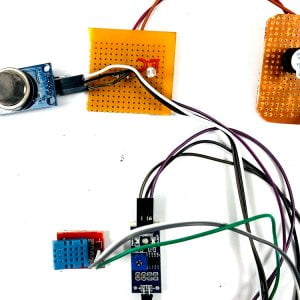
- DHT11 is a two-in-one sensor that can measure both temperature and humidity
- MQ135 is used for monitoring different gaseous elements in the air
- MQ135 is an analog sensor so it needs to be connected to an analog pin
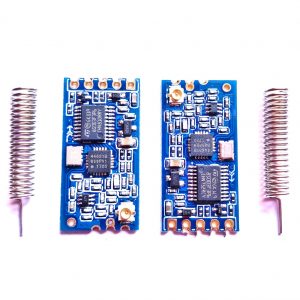
- Lora is connected serially
- In the data collecting node, Node MCU is connected to PC through UART communication
HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS
- Node MCU ESP8266
- LoRa module
- DHT-11
- MQ135
SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS
- Programming platform: Arduino IDE
- Programming language: Embedded C
REFERENCES:
- B. Adam B, A. Kumar J and R.Kumar ?Lora Based Intelligent Home Automation System?, International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT), Vol.6 Issue-3, February 2017.
- A. Al-Fuqaha, M. Guizani, M. Mohammadi, M. Aledhari and M. Ayyash, “Internet of Things: A Survey on Enabling Technologies, Protocols, and Applications,” IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 2347-2376, Fourth quarter 2015.
- A. Koren and D. ?immune?, “Modelling an energy-efficient ZigBee (IEEE 802.15.4) body area network in IoT-based smart homes,” 2018 41st International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics, and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, 2018, pp. 0356-0360.
- A. J. Wixted, P. Kinnaird, H. Larijani, A. Tait, A. Ahmadinia and N. Strachan, “Evaluation of LoRa and LoRaWAN for wireless sensor networks,” 2016 IEEE SENSORS, Orlando, FL, 2016, pp. 1-3.
- Juha.P, K.Mikhaylov, M.Pettissalo, J.Janhunen and J.Iinatti ?Performance of a low-power wide-area network based on LoRa technology: Doppler robustness, scalability, and Coverage?, International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2017, Vol. 13(3).












































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Customer Reviews
There are no reviews yet.