Description
Ground Water level Prediction using Machine Learning
In this project work, we perform an analysis of groundwater level data in three districts of Tamilnadu. We have analyzed this data for more than 100 observation wells in each of these districts and developed seasonal models to represent the groundwater behavior. Three different types of models were developed-periodic, polynomial, and rainfall models. While periodic and polynomial models capture trends on water levels in observation wells, the rainfall model explores the correlation between rainfall levels and water levels. The periodic and polynomial models are developed only using the groundwater level data of observation wells while the rainfall model also uses the rainfall data. All the data and the models developed with a summary of the analysis are available at [1]. The larger aim is to build these models to predict temporal changes in water level to aid local water management decisions and also give region-specific input to Government planning authorities e.g. Groundwater Survey and Development Agency to flag water status with more information. Ground Water level Prediction using Machine Learning
Introduction:
Water below the land surface appears in two zones – saturated and the unsaturated zone. When rainfall occurs, a part of it infiltrates into the ground. Some amount of this infiltrated rain is held up by the upper layer of soil in its pore spaces. This layer is immediately below the land surface and contains both air and water and is known as the unsaturated zone. When all the soil pores are completely filled with water, then water seeps further down through the fractures in the rock. After a certain depth, all pores in the soil are completely filled with water, this part forms the saturated zone. The top of the saturated zone is known as the water table and the water in this zone is called the groundwater. Figure 1.1 shows the saturated and unsaturated zone.
Existing System
The groundwater level is an indicator of groundwater availability, groundwater flow, and the physical characteristics of an aquifer or groundwater system. Due to increased population and decreased groundwater recharge, the demand increases and it may not be feasible to check the draft of groundwater resources. The only available option is to increase the recharge rate to the aquifer by suitable means. Therefore it is necessary to quantify the present rate of groundwater recharge, monitor the change in water table depth, and then predict the future trend of water table depth before any intervention.
Disadvantage:
- Any phenomenon, which produces pressure change within an aquifer, results in the change of groundwater level.
- These changes in groundwater level can be a result of changes in storage, amount of discharge and recharge, variation of stream stages, and evaporation.
Proposed System
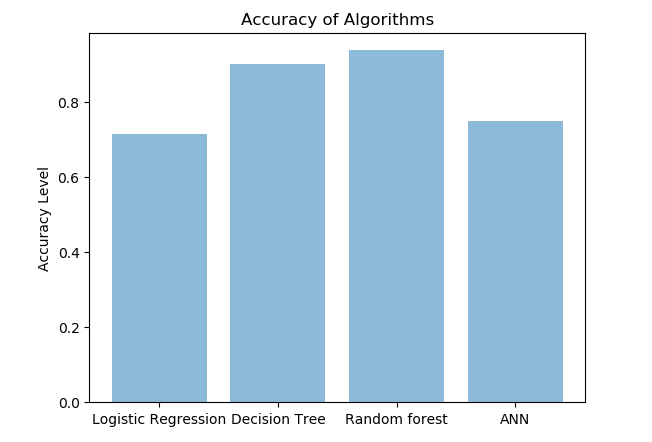
This is mainly in the form of estimation of the magnitude of hydrological parameters. The factors that influence and control the groundwater level fluctuation were determined to develop a forecasting model and examine its potential in predicting groundwater level. Models for the prediction of water table depth were developed based on Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) with different combinations of hydrological parameters. The best combination was confirmed with factor analysis. The input parameters for groundwater level forecasting were derived using Time Series Analysis (TSA).
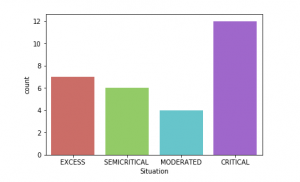
Advantage
- Most of the researchers used ANN alone to predict groundwater levels.
- But the present study incorporated factor analysis along with time series forecasting to increase the accuracy and usefulness of prediction.
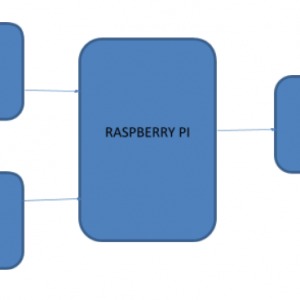
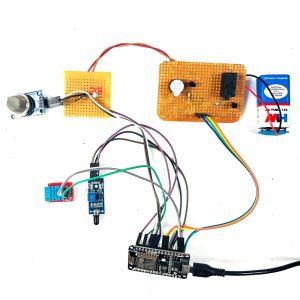
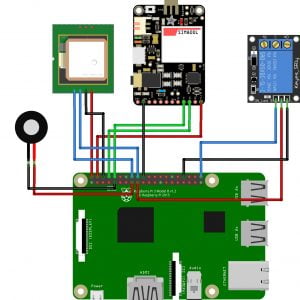
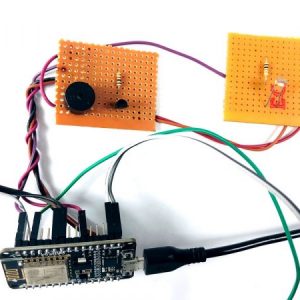
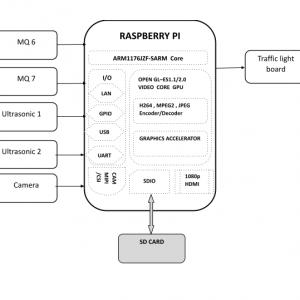
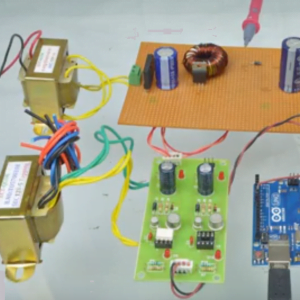
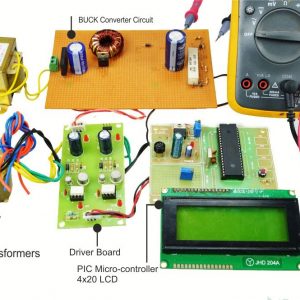
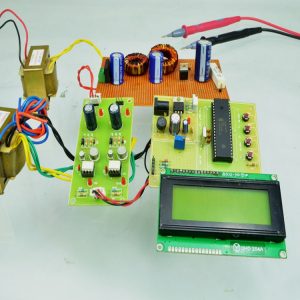
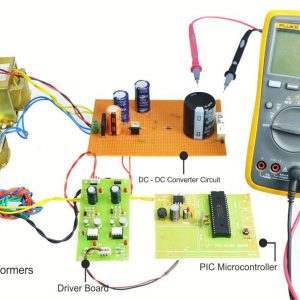
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
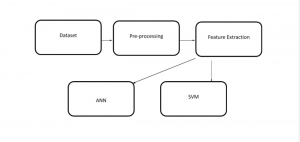
Software:
- Python 2.7
- Anaconda Navigator
Python’s standard library
- Pandas
- Numpy
- Sklearn
- tkMessageBox
- matplotlib

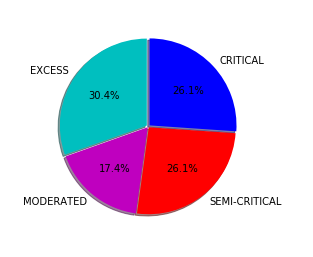
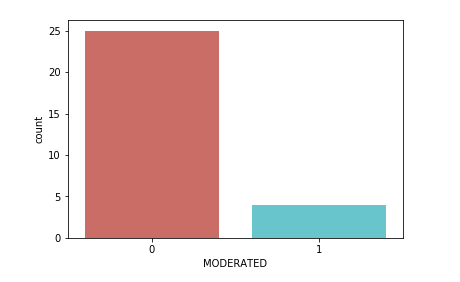
































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































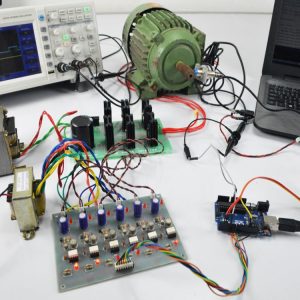

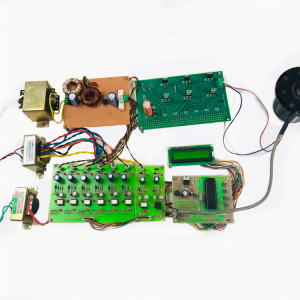
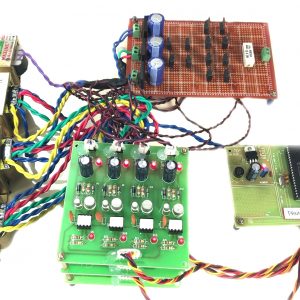
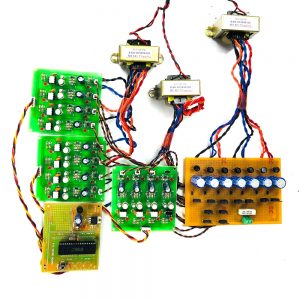
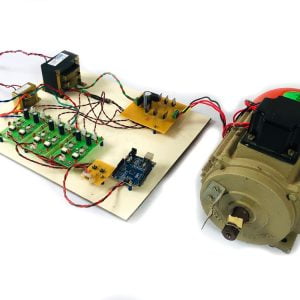
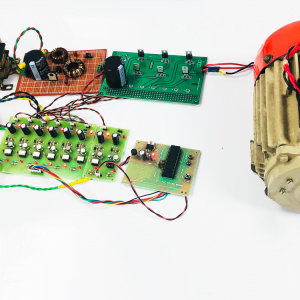

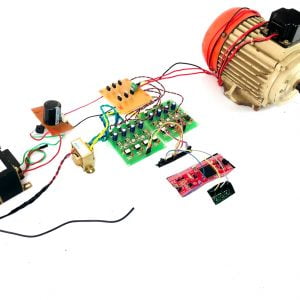
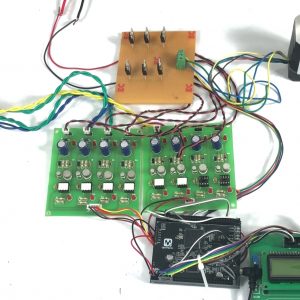










































































































Customer Reviews
There are no reviews yet.