Description
Accurate Shadow Detection and Removal from High-Resolution Satellite Images
Abstract:
High-resolution satellite images contain a huge amount of information. Shadows in such images generate real problems in classifying and extracting the required information. Although signals recorded in the shadow areas are weak, it is still possible to recover them. Significant work is already done in the shadow detection direction but, classifying shadow pixels from vegetation pixels correctly is still an issue as dark vegetation areas are still misclassified as a shadow in some cases. Background subtraction is a commonly used method to detect moving objects from videos captured by static cameras. However, shadows and reflections significantly affect the output of background subtraction algorithms and distort the shape of the objects obtained as a result. Thus, shadow detection and removal is a crucial post-processing step to perform accurate object tracking required by different applications. We present a lightweight method to detect and remove shadows as well as reflection effects in indoor and outdoor environments by using spatial and spectral features. This method incorporates an adaptive way to set thresholds to avoid preset numbers. We present a comparison of the outputs we obtained with those of several other methods. The experimental results demonstrate the success of the proposed algorithm. Accurate Shadow Detection and Removal from High-Resolution Satellite Images
Accurate Shadow Detection and Removal from High-Resolution Satellite Images
Introduction
- Imitations are not new to humanity however as an opportunity is very old trouble. In the beyond it changed into restrained craftsmanship and writing but did now not have an effect on the overall population. These days, due to the headway of automatic image handling software programs and changing gadgets, an image can be results managed and changed. It is alternatively tough for people to apprehend outwardly whether or now not or now not the photo is unique or manipulated. There is a speedy increment in digitally controlled falsifications in great media and on the Internet. This sample shows authentic vulnerabilities and abatements of the credibility of digital photographs. In this manner, growing techniques to check the honesty and realness of the superior snapshots is essential, especially considering that the picture is delivered as evidence in a courtroom docket of regulation, as facts things, as part of restorative records, or as coins related opinions. Here the shadow which is present in the satellite images is going to remove by means of HE, LHE, AHE, and CLARE. These are all used in this project and finally, we get a clear image without the presence of shadows. Accurate Shadow. Detection and Removal from High-Resolution Satellite Images
System Analysis
Existing Systems
- Compensation,
- Principal component
- Shadow threshold.
Drawbacks
- In appearance-based methods, less accurate features description because of whole
- Image consideration
- Difficult to get accurate results
- Time Consuming
- Not applicable for multiple images for pattern detection in a short time
Proposed System:
We have proposed a new method for image equalization which is an extension of HE, LHE, AHE, and CLARE is used to enhance of the low contrast of the image.
Advantages
- The histogram equalization method may result in over enhancement and saturation artifact.
- Histogram equalization can be found in the fact that it may significantly alter the brightness of an image
Accurate Shadow Detection and Removal from High-Resolution Satellite Images
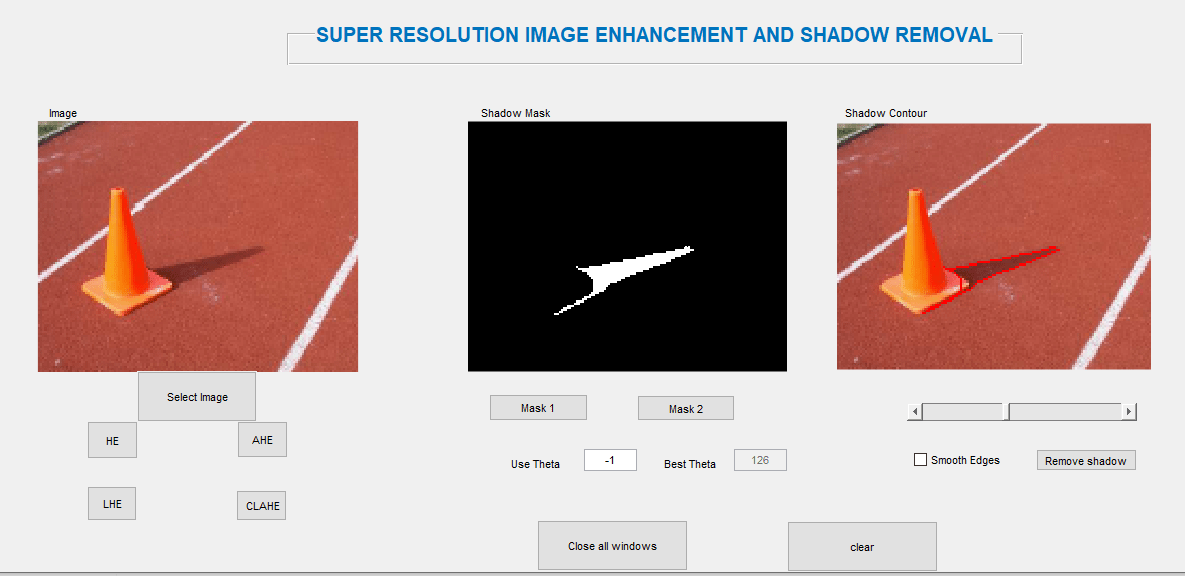
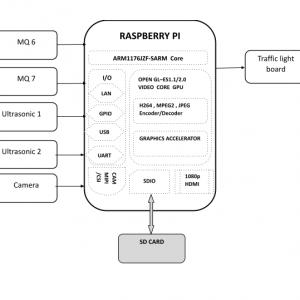
Block Diagram
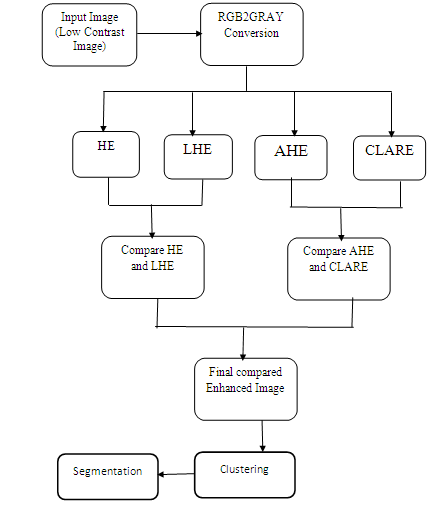
Accurate Shadow Detection and Removal from High-Resolution Satellite Images
IMAGE ACQUISITION
Image Acquisition is collecting a digital photograph. To collect this requires a picture sensor and the functionality to digitize the sign produced thru the sensor. The sensor might be a monochrome or coloration TV camera that produces an entire photo of the trouble area each 1/30 sec. The photograph sensor may also be a line test virtual digicam that produces a single photo line at a time. In this situation, the gadgets move beyond the road.
Histogram equalization
Histogram equalization is a method of improving the contrast globally. This process is the adjustment of intensity which is globally distributed across the image. If we consider any grayscale image (x),?be the number of occurrences of gray level I and a probability function of the occurrence of a pixel of level I in the image (x) is

In Fig 4.3, the gettable HSV colors lie among a triangle whose vertices area unit outlined by the 3 primary colors in RGB space:

Fig4.3: Obtainable HSV color from RGB color space
The hue of purpose| P is the measured angle between the road connecting P to the Triangle center and the line connecting RED point to the Triangle center. The saturation of the purpose P is the distance between P and the triangle center. The value (intensity) of the purpose P is depicted as height on a line perpendicular to the Triangle and spending through its center.
The grayscale points area unit is located on a similar line. and therefore the conversion formula is as follows:

Hardware Requirements
- system
- 4 GB of RAM
- 500 GB of Hard disk
SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS:
- MATLAB 2018b
Accurate Shadow Detection and Removal from High-Resolution Satellite Images
REFERENCES:
[1] T. F. Y. Vicente, L. Hou, C.-P. Yu, M. Hoai, and D. Samaras, ?Largescale training of shadow detectors with noisily-annotated shadow examples,? in Computer Vision? ECCV 2016, B. Leibe, J. Matas, N. Sebe, and M. Welling, Eds. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016, pp. 816? 832.
[2] J. Wang, X. Li, L. Hui, and J. Yang, ?Stacked conditional generative adversarial networks for jointly learning shadow detection and shadow removal,? CoRR, vol. abs/1712.02478, 2017.
[3] J. Zhu, K. G. G. Samuel, S. Z. Masood, and M. F. Tappen, ?Learning to recognize shadows in monochromatic natural images,? in 2010 IEEE Computer Society conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2010, pp. 223? 230.
[4] D. Kersten, D. C. Knill, P. Mamassian, and I. Blthoff, ?Illusory motion from shadows,? Nature, vol. 379, no. 31, 1996.
[5] S. Jiddu, P. Robert, and E. Marchand,?Estimation of position and intensity of dynamic light sources using cast shadows on textured real surfaces,? in 2018 25th IEEE Int. conf. on Image Proc. (ICIP), 2018, pp. 1063? 1067. [6] Y. Zhang and D. Zhu,?Height retrieval in postprocessing-based VideoSAR image sequence using shadow information,? IEEE Sensors J., vol. 18, no. 19, pp. 8108? 8116, 2018.















































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































Customer Reviews
There are no reviews yet.